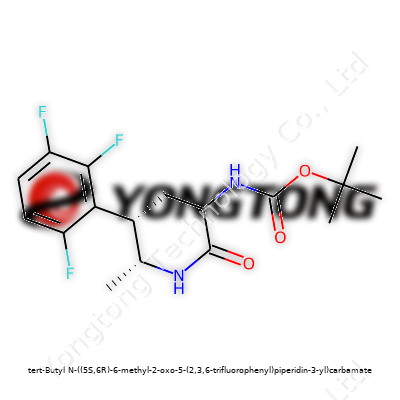
Tert-Butyl N-((5S,6R)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl)carbamate: A Ground-Level Analysis
Historical Development
Chemists keep pushing for better tools and sharper weapons, and the rise of compounds like tert-Butyl N-((5S,6R)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl)carbamate tracks right along with that drive. Early on, labs dug into the piperidine core—six-membered rings with a nitrogen twist—chasing molecules that could serve both the mind and body, through routes like pain management or receptor modulation. As pharmaceuticals started leaning on “fluoro” tweaks to pump up potency and help drugs dodge metabolism, trifluorophenyl branches started popping up all over research grids. The N-Boc protection strategy—using tert-butyl carbamate to lock down nitrogen atoms during synthesis—caught on with anyone steering volatile building blocks through rough reaction waters. This chemistry didn’t drop out of the sky last year. It built up as scientists, from academic corners to pharma giants, layered old-school discovery with sharper, smarter synthetic steps.
Product Overview
To the layperson, this compound sounds like chemistry run amok. Its name maps to a precise shape: a piperidine backbone, a pair of stereocenters dictating how it behaves, and a carbamate group standing guard over its sensitive nitrogen. A big, bulky tert-butyl shield at one terminus resists unwanted reactions, while that trio of fluorine atoms adds bite—tuning electronic properties, slowing down metabolic breakdown, and sometimes blocking off specific reactions. Most labs handle it as an intermediate—a halfway house on the path between raw material and finished API, though some research teams peer into its biological promise on its own.
Physical & Chemical Properties
Take this molecule off the page, and you find it lands on the bench as a solid—white to off-white, crystalline and dense. Its molecular weight clocks in above 370 g/mol, a size that feels right for a target in early drug development. Melting points hover between 130–150°C, often depending on the subtle impurities from previous steps. Water won’t budge it, but DMSO and other polar aprotic solvents dissolve it fast—a feature that prompts careful handling and specific storage needs. Fluorinated aromatic rings, a rigid carbamate, and a well-defined stereochemistry keep this molecule stable during most routine manipulations and make it compatible with pretty standard purification methods, though chromatography always finds a way to separate subtle byproducts.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Researchers don’t accept maybes—they want full documentation, lab analysis, and total transparency. Vials of this carbamate get labeled with full technical sheets: stereochemistry, batch number, precise purity (measured down to the tenth of a percent), and a suite of identity checks including NMR, LC-MS, and IR profiles. Any vial crossing international lines needs a batch release certificate and adherence to regulated shipping temperatures. Purity standards above 98% are table stakes, ensuring contaminants don’t muddle up bioassays or clinical development. The label spells out not just the technical specs, but clear hazard indicators too, recognizing both the regulatory expectations and the hands-on reality of modern research settings.
Preparation Method
Lab cooks draw up procedures with every step mapped out, prepping the starting piperidine core through hydrogenation, halogenation, and regioselective substitution before wiring in the trifluorophenyl ring. Stereoselective reduction and precise functional group installation keep the configuration locked. Coupling with tert-butyl carbamate, often driven by activating agents like EDCI or DCC, forms the protected carbamate—usually in the final third of the process to shield sensitive nitrogens from stray nucleophiles or acids. Each reagent, from base to solvent, brings its own baggage: purity, yields, and the headaches of safe disposal. The finishing touch includes deep drying and a battery of tests to rule out racemization or side products, locking in the specifications needed for downstream work.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
Working with this carbamate isn’t a dead end. Chemists can snip off the Boc group using TFA or mild acid, freeing up a naked amine for further coupling, labeling, or cyclization. Aromatic fluorines sometimes trade places with nucleophiles in aromatic substitution reactions, expanding its reach into new analogues. Modifications on the methyl, carbonyl or piperidine ring let medicinal chemists pull this structure into new spaces, controlling lipophilicity, tweaking metabolic stability, and targeting better receptor affinity. Every tweak brings risk and reward: altering potency, solubility, and sometimes bringing out toxicity or improved safety profiles.
Synonyms & Product Names
Molecule naming drifts between clarity and chaos. Suppliers use systematics for paperwork but drift toward short-hand on shelves. “Boc-(5S,6R)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-ylcarbamate” or “N-Boc-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl) piperidin-3-ylamine,” for short, make appearances across catalogs, while some labs coin their own abbreviations for sample management. CAS numbers remain a universal signal, even when local systems demand their own tweaks.
Safety & Operational Standards
Chemists hate surprises in the fume hood, so they work with gloves, goggles, and the usual PPE, treating all carbamates with respect. While most batches stay well-behaved, powerful solvents or strong acids in its prep demand care. Direct handling stays at a minimum, with powder transferred in closed vessels and spills caught with inert absorbents. Waste procedures follow clear lines: carbamates go to chemical incineration, fluorinated byproducts queue for special disposal, and nothing gets piped down regular drains. Material safety data sheets spell out everything from storage conditions to first aid steps, putting human health and work safety on equal footing.
Application Area
In the real world, compounds like this carbamate stick close to early-phase drug development and SAR campaigns inside pharma labs. Researchers count on its stable protected amine to sidestep unwanted side reactions, using it to build larger, more complex molecular scaffolds. Its unique stereochemistry and the electronic impact of the trifluorophenyl group open doors for neurological, metabolic, or even cancer-targeted molecules. Biologists tap into analogues for in vitro screening, hunting activity at receptors like the opioid, dopamine, or serotonin families. Materials scientists sometimes explore fluorinated piperidines for their hydrophobicity and stability, driving interest into sectors beyond pharma, though challenges of scale and toxicity keep the focus rightfully tight.
Research & Development
Every dollar spent in the lab traces back to breakthroughs and setbacks. Pharma companies keep tuning this class of carbamates to beat drug resistance or reach patients that older molecules miss. By altering stereochemistry and tweaking substituents—especially adding or changing fluorines—researchers can sometimes sidestep metabolic breakdown, lengthen half-life, or sharpen selectivity. The compound’s resilience under acidic or basic conditions supports parallel synthesis, where analogues sprout in weeks instead of years, filling the drug discovery funnel. Preclinical profiling asks for solid, reliable intermediates, and the synthetic flexibility of compounds like this one pays off in hands-on research, driving both academic publications and patent filings.
Toxicity Research
Labs don’t put blind trust in shiny molecules. Chemists and toxicologists tackle cytotoxicity, looking for red flags in cell viability or enzyme activity. Carbamates catch extra attention for potential off-target effects, since some related types can release isocyanates or reach into the cholinesterase pathway, sparking concern over bioaccumulation or chronic exposure. Animal models help, but in-vitro assays remain the first checkpoint, screening for genotoxicity, acute toxicity, and allergic potential before anyone thinks about moving toward the clinic. Regulatory authorities in Europe and the States hold manufacturers and researchers to updated thresholds, so ongoing investment in safety research determines if this molecule stays a lab curiosity or lands in a pharma pipeline.
Future Prospects
The road ahead for such advanced carbamate intermediates runs through both creative organic synthesis and realism about commercial scale. Academic labs continue probing new routes to swap out hazardous reagents, chasing greener, higher-yielding preps. Demand won’t slow down as long as pharma R&D churns out new analogues or faces new biological targets. Tools like high-throughput experimentation and machine learning promise to fine-tune synthetic steps, raising yields and cutting waste. At the same time, regulatory pressure over persistent fluorinated byproducts keeps industry honest, pressing for recycling and non-toxic disposal plans. As more data comes in about metabolic fate and long-term risk, the science community can either double down on this class or pivot toward less persistent alternatives, keeping safety, efficiency, and patient benefit front and center.
Where Chemistry Meets Healthcare
tert-Butyl N-((5S,6R)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl)carbamate doesn’t roll off the tongue, but for people working in drug discovery, this sort of chemical marks more than a mouthful of syllables. The backbone of this molecule ties together two worlds: serious laboratory research and the hope for genuine breakthroughs in fighting illness like obesity, diabetes, and even some rare genetic disorders.
Roots in Scientific Progress
At the bench, people know this compound best as a building block or “intermediate” in the race to create active drug ingredients. It shows up during the step-by-step process where complex medicines take shape. In recent years, the piperidin-3-yl core joined with these fluorinated rings has caught attention for how it helps lock molecules into useful structural shapes – nudging them toward better stability and stronger effects in the body.
Plenty of research points to this structure as a critical intermediate for compounds aimed at controlling the effects of the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), a target linked to appetite and energy control. Drug designers have built synthetic routes around this carbamate for one reason: it can yield drug candidates showing promise in weight management and treatment of rare forms of inherited obesity. Since 2023, news about MC4R research puts drugs like setmelanotide in the news, thanks to the FDA’s approval of this type of compound after decades of slow progress.
Why Specific Structure Matters
In my own years reading chemical patents and digging through pharma pipelines, I’ve watched as research teams return again and again to these fluorinated side groups—the trifluorophenyl ring—for a reason. Small changes like that can make or break a drug’s chances in animal tests and later in human trials. Fluorine atoms often transform how long a drug sticks around in the body, how it dodges breakdown by enzymes, or how precisely it fits the intended receptor. So, when chemists build out the structure of new MC4R modulators, this carbamate forms a solid foundation for more complex designs.
Bigger Picture: Medicines in the Making
Right now, clinical trial teams and medicinal chemists keep searching for more effective, targeted weight loss drugs. The rise of semaglutide and tirzepatide highlights a new competitive era among metabolic therapies, but options still fall short for genetic and rare metabolic disease. Chemicals like tert-Butyl N-((5S,6R)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl)carbamate carry real weight here, because they serve as the raw material for testing dozens, if not hundreds, of slightly different drug candidates.
Narrowing down to one winning molecule often takes years. Experienced researchers often talk about the long haul—testing, tweaking, and retesting to dodge side effects or improve performance. Each intermediate, each carbamate, gets its moment in the spotlight as teams search for better options in treating conditions with real patient impact.
Solving Bottlenecks in Drug Innovation
From talking to friends in the lab and reading industry news, I keep hearing calls for smoother, faster paths from promising chemistry to real-world medicine. Reliable sourcing for synthetic intermediates remains a problem; sudden supply chain gaps still slow down labs working on orphan diseases. Partnerships between academia, startups, and big pharma stand out as one answer—sharing the load of scaling up these specialty chemicals and making sure they’re available for anyone with a good idea and the right clinical data.
The world wants safer, targeted therapies for conditions of metabolism. It makes a genuine difference when these humble intermediates get the attention they deserve. In the end, the people who benefit most are those waiting for new medications with fewer side effects and a better shot at lasting health.
Cold, Dry, and Out of the Sun: The Foundations of Stability
Whether in a university lab or a pharmaceutical warehouse, most people start with a few basics. Many compounds don’t last long when heat and humidity sneak in. I once watched a colleague struggle through a research project because we stored a batch of sensitive powder near a sunny window. The degradation crept in quietly—suddenly, test results lacked punch, and we had to throw out an entire month’s work. For something whose potency matters, such as a medicine or reagent, experienced scientists know to keep the container tightly closed and away from light. Even a little carelessness can change the story of the compound inside.
The Enemy: Moisture, Light, and Heat
Water finds its way everywhere. Suppose a material absorbs moisture from the air. With time, it clumps, changes color, or begins to react before you’re ready. That comes with risks for labs and users. Pills lose effectiveness; chemicals break down into shapes and structures that don’t behave as expected. In my years of handling compounds, I’ve seen some go sticky in a matter of days because they lived above a sink or near a door that opened too often. Humidity often shortens shelf life and safety margins.
Direct sunlight breaks chemical bonds. You might notice a faint smell, a yellowing powder, or a shift in crystal form. One summer, a chemical drum left near a skylight ended up useless—light did its quiet, relentless work, and we learned to rely on shaded shelves. Sunlight rarely forgives such oversights.
Beyond the Label: The Cost of Wrong Choices
Ignoring storage guidelines leads to more than spoiled inventory. A pharmaceutical staffer once told me about a batch lost to heat during transport. The replacement costs strained the budget, but unseen changes carry even more risk. Potency can fade, toxicity may rise, side effects grow unpredictable. A storage mistake can ripple through to product recalls or, worse, patient harm. Police labs and drug manufacturers operate under strict controls for a reason.
Temperature Matters More Than It Seems
Refrigerated storage isn’t about comfort; it’s protection from the slow, invisible hand of chemical change. Most chemicals prefer temperatures between 2°C and 8°C, but some freeze at those levels or form crystals that block nozzles and vials. Room temperature means different things in Florida and Finland. Many companies use climate-controlled spaces with alarms that shriek if temperatures wander, investing hundreds or thousands of dollars in backup systems. Without these, all the science and money poured into discovery can disappear in a power outage or heatwave.
Solutions that Stand the Test of Time
Simple steps prevent most storage issues. A clean, dry, and dark space beats the fanciest setup if people use it consistently and label everything with dates and instructions. Silica gel packets in jars, opaque bottles, and regular inspections go far. Electronic logs allow tracking every shipment and alerting staff when conditions drift.
Regulations also play a role. The US Food and Drug Administration, European Medicines Agency, and similar bodies tell companies to validate and document every storage condition. Auditors check logs, measure temperatures, and inspect seals, because contamination, decay, or accidental mixing costs more than anyone likes to admit.
Details Decide the Outcome
Compounds want what they want—ignore that, and you pay for it. Years of lab work, conversations with industry workers, and a few painful losses have taught me that stability doesn’t come from guesswork. Read the label. Invest in good storage tools. Make routine checks a part of daily life. That’s where safety and reliability grow.
The Real Importance Behind Chemical Data
Every time someone asks for the molecular formula and weight of a product, most folks probably imagine a dry string of letters and numbers. Those numbers actually stand for deeper meaning, carrying real-world significance in everything from developing pain medicine to ensuring the snacks in your cupboard don’t spoil. At a glance, it looks simple: something like C6H12O6 points to glucose, with a molecular weight of about 180.16 g/mol. But those few symbols tell us a lot. They inform shelf stability, dosage safety, and whether a compound actually helps instead of harms.
Just in my time working next to food labs and pharma reps, I’ve watched seasoned experts pause a conversation for a five-second debate over a formula. Getting it wrong risks pricey recalls or flawed clinical trials. If a chemist writes down CH2O for formaldehyde and means C2H4O for acetaldehyde, all sorts of confusion starts. The molecular formula doesn’t just summarise a product; it gives production teams guidance on what actually shows up in the factory drum. One mistake in the weight could throw off calibration in a machine, leading to bottles filled with too much or too little of an active ingredient.
How Accurate Data Builds Trust
Beyond industry walls, this level of chemical detail helps society trust what goes into our bodies and onto our plates. If you want to know why a product label shows a long list of numbers, thank the regulatory watchdogs who push for transparency. The right molecular weight, for example, helps manufacturers calculate exactly how much of a vitamin or antibiotic ends up in each batch. In drug research, the formula tells scientists how a molecule breaks down in the body, influencing everything from side effects to efficiency.
My own grandfather, after years of wrestling with diabetes, followed advice rooted in molecular knowledge. Understanding a compound’s structure and weight let his doctors fine-tune his treatment plan. It wasn’t flashy—just a calculation on a chart during an appointment—but that simple number kept his blood sugar from spiking out of control. Without that detail, treatment would have felt like a roll of the dice.
Better Access and Fewer Mistakes
Mistakes and miscommunication over chemical formulas can spark major public health scares or bring a company’s operations grinding to a halt. During an outbreak investigation linked to tainted food, it’s often the product’s precise formula and calculated weight that determines how fast authorities can pull unsafe items from store shelves. Having clear, accurate data in databases—checked and cross-referenced, not copied and pasted—protects everyone from small-time kitchen accidents to million-dollar mishaps in global supply chains.
Looking for Solutions in Communication
One solution starts with better communication between research teams and factory crews. Chemists need to talk plain words when passing along molecular data, so the meaning sticks with the next worker down the line. Digital tools that flag inconsistencies in formulas before they reach a client can stop mistakes before they become headlines. Universities and training programs must drill real-life examples, showing why knowing C6H12O6 is the backbone of an energy drink or helps a nurse manage insulin doses. Those connections make chemistry less like a trivia contest and more about protecting health and business.
Making Sense of Purity in Real Life
People like to know what they are getting, especially with chemicals. The meaning of “purity” goes far beyond some lab perfection. In the supply world, purity changes everything. Think of table salt from the grocery store and the sodium chloride med schools keep locked up; both look the same, but one batch ends up in bread dough, while the other determines the outcome of complicated cell cultures. This difference shapes costs, trust, and safety.
Behind the Label: Who Decides What Counts as Pure?
Not every drum, bag, or bottle stamped with a chemical name packs the same punch. Pharmacopeias set rules for medicines. Tech companies demand levels that detect flaws invisible to the naked eye. School labs often get a “lab grade” that has a bit more wiggle room, both for safety and price.
My own work in research taught me to look past labels. Stories float around labs of unexpected results traced back to overlooked impurities. One time, our organic synthesis failed and the culprit turned out to be a minuscule contaminant. That taught us purity directly affects outcome. Researchers double-check paperwork, compare batch-to-batch, and sometimes insist on certificates that chase each impurity down to the millionth part.
How Purity Impacts Real World Outcomes
Pharmaceutical companies stand on strict purity requirements because a side contaminant can threaten lives. Food producers stay on alert, too. Sugar that lands in drinks faces international regulations; one batch heading for a soft drink will probably get a closer look than sugar used for some local candies. Electronics makers source chemicals that push up against theoretical limits of purity, as flaws can break expensive hardware.
Chemicals with higher purity call for more time, more checks, and higher costs. It’s not an exaggeration—one percent difference in purity sometimes doubles the price tag. That plays out everywhere, from small research labs running on grants, to giants in semiconductors chasing the next smallest chip. Suppliers clued into this reality offer several “grades.” Even for consumer goods, corners cut during refining stick out in flavor, color, or shelf life.
Judging What’s Needed
The smartest thing anyone handling chemicals can do? Match the grade to the job. Knowledge does not stay behind locked lab doors. Reputable suppliers clearly publish specifications and keep safety documents up to date. Responsible users ask tough questions before buying anything in bulk. Regulatory agencies publish recall lists when the wrong grade slips through or new tests reveal hidden issues.
Every scientist, engineer, or chef ends up balancing safety, performance, and cost. Training sharpens these choices, but only experience teaches the small details that make up purity: odd odors, unexpected residue, failures so small they show up only after hours of effort. Still, aiming for honesty and transparency about what “pure” means pays dividends. Problems shrink, accidents dip, and trust gets built batch by batch.
Raising the Bar for Everyone
Anyone in the supply chain who dismisses purity as marketing misses the lessons learned over years of mishaps and close calls. Direct communication between user and supplier pushes everyone to do better. People counting on safe, reliable products downstream count on those standards being met—for reasons bigger than one line item on a receipt. This keeps everyone a little safer, a little more confident, and a lot better off in the long run.
Why Caution Matters
A lot of folks look at warning labels and think, “That’ll never happen to me.” Yet, the smallest mistake can send someone to the emergency room. Out on job sites, I’ve seen injuries from shortcutting safety gear—burns, rashes, and worse. I remember a coworker splashing a cleaning chemical on his skin because gloves seemed “too much.” He thought he’d wash up and go on, but the skin burned for days. Nobody expects accidents, but staying careful always wins.
Precautions That Actually Work
Three things stand out for me: personal protective equipment, clear workspace practices, and good storage habits. Gloves aren’t just for doctors and mechanics—they save your skin from burns, cuts, and even hidden chemical reactions. Goggles and face shields keep splash injuries out of your day—your eyes don’t heal like skin. Long sleeves and closed shoes form your second layer of defense when things go sideways.
Ventilation deserves real respect. I spent some time in a paint shop where fumes, even from “safe” products, built up fast. Fresh air flushes dangerous gases and dust so your lungs don’t have to process them later. If outside ventilation isn’t possible, local exhaust, like a fume hood or extractor fan, cuts down the risk.
Watching Out for Unexpected Dangers
Labels tell an important story. Products might look like soap, but their chemical makeup could burn, poison, or explode with a careless move. Reading the label and checking the safety data sheet before opening a new bottle becomes a habit when you’ve seen what goes wrong behind closed emergency room doors. Many manufacturers break instructions into clear steps. Following those lines is a lot safer than guessing.
Never mix chemicals on a hunch. Bleach and ammonia, for example, create toxic gas if they meet in your mop bucket. Even mixing strong acids with water requires the right order—acid goes into water, not the reverse. Heat and splatter catch even the careful off-guard when steps get skipped. Stick to one chemical at a time, rinse and clear the workspace before switching, and take time to double-check.
Cleaning Up the Smart Way
I once saw a spill cleaned with paper towels and tossed in the trash—hours later, the bin smoldered from spontaneous combustion. Oil rags, chemical-soaked cloths, and even some solvents keep reacting after they seem “used up.” Waste containers with tight lids, and separate storage for different types of waste, stop accidents before they start. Following local disposal guidelines protects people and the environment downstream.
Keeping Information Handy
A posted safety data sheet and a practiced eye can stop a bad day from turning tragic. Keeping emergency contact info, eyewash, and showers nearby keeps everyone moving safely. Training doesn’t end after the hiring orientation. It sticks through repeating drills, swapping stories, and reminding each other to suit up and slow down.
At the end of the day, protecting yourself with the right tools and knowledge isn’t just for insurance. It’s for friends, families, and everyone who counts on coming home healthy. Real safety comes from staying alert, not cutting corners, and respecting what you work with, every single time.