Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid: A Closer Look at Its Past, Present and Future
Historical Development
Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid comes from a long line of amino acid derivatives, with roots that dig back into the golden years of peptide chemistry in the twentieth century. Researchers have always searched for more stable, selective, and functionally flexible building blocks. The backbone of this compound—an amino acid protected by the tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) group—became popular as chemists learned that such protection could lend stability during peptide synthesis. The trifluorophenyl arm started drawing more attention when medicinal chemists noticed how fluorine atoms influence molecular recognition and metabolic resistance. The story of Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid ties into this push for new synthetic tools. Every advance in protecting-group chemistry, asymmetric synthesis, and organofluorine development set the stage for making and using this molecule in research and industry.
Product Overview
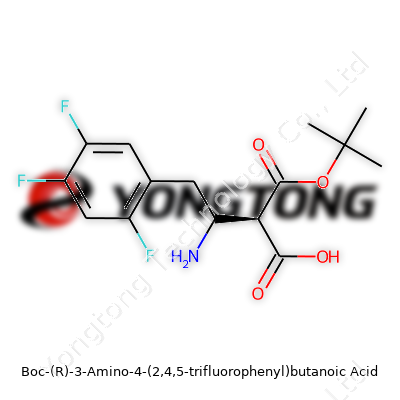
Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid serves as an intermediate in pharmaceutical development, especially for those chasing new leads in peptide-based therapeutics and enzyme inhibitors. Companies list it under various catalog names and stock it as a white to off-white solid. Its structure combines a Boc-protected amino group with a butanoic acid skeleton, carrying a 2,4,5-trifluorophenyl substitution. In my own work, I found that such fluorinated rings often change the ways molecules behave in cell assays and chemical reactions, making them valuable when a subtle tweak can mean the difference between a dead-end and a promising avenue. As interest in fluoro-organics grows, inventory demand echoes that in both research and pilot manufacture settings.
Physical & Chemical Properties
Physically, the compound appears as a crystalline solid. Its melting point commonly lands in the range expected for Boc-protected amino acids, hovering just above 100°C. Aromatic rings decorated with fluorine tend to boost molecular weight and acoustic properties. On the chemical side, the Boc group shields the amine against unwanted reactions, only coming off in acidic conditions. The three fluorines change the electron density across the ring, making the core resistant to metabolic oxidation and providing a useful handle in drug metabolism studies. Standard solubility matches most peptide intermediates, favoring polar aprotic solvents during synthesis and purification. The acid proton on the butanoic chain also allows for salt formation, which helps with formulation tasks or when adjusting for specific downstream protocols.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Each vial or jar usually carries labels with batch number, purity (often >98% by HPLC), molecular weight (319.26 g/mol), and specific rotation ([α]D20 values). The storage recommendation appears: keep it dry, away from light, and at temperatures below room temperature. Inspection certificates should confirm identification by proton NMR, carbon NMR, and mass spectrometry, with certificates of analysis available on request. From my time cataloging such chemicals, I learned that a reliable supplier always goes beyond just the spec sheet, providing documents to cover traceability and compliance for quality management reviews and audits.
Preparation Method
Synthesis of Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid builds on routine solid-phase and solution-phase strategies. The essential steps start with introducing the trifluorophenyl group, usually by coupling a substituted benzene precursor with a suitable keto acid, followed by asymmetric hydrogenation or enzymatic reduction to set the chiral center. Boc protection is added through reaction with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate under mild base. Careful work-up ensures clean isolation, often involving trituration and chromatographic purification. In my own group, troubles often came from incomplete Boc protection or over-reaction on the aromatic ring. A steady hand and real-time TLC tracking made the difference between successful, scalable batches and frustrating repeats.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
This amino acid stands out for what it can do during peptide chain assembly. It undergoes standard peptide-coupling reactions with carbodiimide reagents or uronium activators, smoothly linking into growing chains on solid or liquid supports. After peptide extension, deprotection of the Boc group by mild acid releases the free amine, opening up options for further derivatization. The trifluorophenyl ring grants extra stability, which means peptides incorporating this unit resist some oxidative enzymes. Chemical modification options include transformation of the carboxyl to amides, esters, or the adoption of fluorescent or biotin tags onto the ortho or para positions of the aromatic ring—useful in biological labeling and tracking. Through many late nights in the lab, I’ve seen colleagues turn such modifications into custom affinity tools or enzyme probes, showing what’s possible with good functional handles.
Synonyms & Product Names
Different suppliers and researchers use alternate names: Boc-(R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butyric acid, N-Boc-(R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic acid, or tert-butoxycarbonyl-(R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic acid. Less formally, it might be called Boc-trifluorophenylaminobutanoic acid. Catalog codes streamline ordering (e.g., TFA-ABoc-R) in chemical supply chains, but proper systematic names and identifiers help avoid the kind of costly mix-ups that haunt peptide campaigns.
Safety & Operational Standards
Handling Boc-protected amino acids always demands gloves, lab coat, and good airflow—even more so with fluorinated compounds. Fortunately, this product stays solid at room temperature, limiting vapor exposure. Splashing, inhalation, or accidental ingestion all require immediate safety steps, following the SDS details. In my experience, the biggest risks come during scale-up when larger solvent volumes and energetic reagents get involved. Following Good Laboratory Practice, including using closed weighing containers and having spill kits within arm’s reach, minimizes risk. Waste disposal needs special attention since fluorinated byproducts can complicate routine organic waste handling and some institutions treat them as higher hazard.
Application Area
Medicinal chemistry has the strongest appetite for Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid. Its trifluorophenyl motif alters how peptides and peptidomimetics interact with protein targets, offering designers a tool for improving potency or metabolic half-life. Drug screening libraries, structure-activity relationship studies, and bioconjugation protocols all use this acid as a critical piece. Research teams in neuroscience, oncology, and infectious disease often look for building blocks with such fluorinated rings to tip the balance against fast-acting enzymes. I remember one cancer drug campaign where replacing a hydrogen with a fluorine on a similar scaffold led to a twofold boost in target engagement. Outside pharmaceuticals, the compound contributes to making custom bioanalytical tools and occasionally pops up in materials projects chasing high-performance coatings or adhesives where peptide-mimetic units lend both toughness and versatility.
Research & Development
The research community keeps finding new directions for fluorine-rich amino acid derivatives like this one. Large pharma invests in high-throughput synthesis so that peptide libraries can incorporate various fluorinated backbones, testing new combinations. Academic groups publish on improved synthetic routes, greener protection schemes, and approaches that cut down on toxic byproducts. In some years, a hot topic has been designing analogs to toughen up enzyme inhibitors or to color-tag proteins for imaging without disrupting their natural functions. My colleagues in academia have noted that collaboration between groups working in synthesis, biochemistry, and pharmacology brings real synergy; progress feeds back as new data informs molecular modification strategies.
Toxicity Research
The safety story for Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid resembles many specialty amino acid derivatives. Cell and animal studies tend to show low toxicity at screening concentrations, though care must be taken with metabolites, since some aryl-fluoride byproducts can linger in the environment. Full degradation studies, aquatic toxicity profiling, and animal model trials help clarify safe use lines—especially as regulatory agencies step up demands for data on anything with multiple fluorines in the ring. I’ve seen colleagues run extra LC-MS screens to check for accumulation of any odd metabolites. Only through such due diligence can new compounds clear the bar for broader commercial adoption.
Future Prospects
Growth prospects for Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid stay strong, driven by the need for ever more diverse peptide building blocks, especially in precision medicine and bioconjugation projects. With machine learning now helping predict which modifications will succeed in drug design, fluorinated amino acids remain in demand. Environmental footprint weighs heavier on synthetic strategies, so efforts keep shifting towards methods that recycle protecting groups or avoid harsh reagents. As funding flows into novel peptide therapeutics and sequence-defined materials, chemists—both in academia and industry—stand poised to take advantage of what this acid offers. More sustainable production, smarter design, and tighter links between chemical innovation and biological need could guide its next chapters.
The Reality of Purity in Modern Labs
Stepping into any synthetic lab means coming to terms with purity. For Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid, every chemist searching for reliable results knows pure starting material underpins the whole process. Fresh out of grad school, I learned fast that even the subtlest trace of impurity throws months of work into chaos. This compound, sometimes a mouthful to pronounce, comes up most in peptide synthesis and pharmaceutical development. It’s not just a luxury to pursue top purity—isolation and purification shape the stories behind every successful experiment.
Measuring Purity: Numbers Tell the Story
Manufacturers and researchers report purity for this compound in percentages, with high-grade material clocking in anywhere from 97% up to over 99%. Analytical companies stand by these numbers through validated methods, like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) paired with NMR or mass spectrometry. These days, nobody takes those numbers on faith. Reputable labs publish their chromatograms, batch analyses, and certificates of analysis. Sometimes I have found myself double-checking a supplier’s claims, especially when scaling up or chasing grant money.
Any credible supplier will specify both chemical purity and enantiomeric excess. Only the (R)-enantiomer counts in select pharmaceutical applications—an off-ratio batch throws everything off, wasting more than time or money. The lot of us who have tried separating racemates on a tight deadline know the headaches there. Popular suppliers in both the US and Europe advertise their purity numbers, sometimes as high as 99.5%, but I always look for a full impurity profile, not just that top number.
Why Real Purity Matters
Making early mistakes in the lab made it crystal clear: purity changes yields, reproducibility, and even patent rights. Any small unknown peak on a chromatogram raises red flags for bioactive work. In drug development, for instance, impurities above 0.1% can trigger toxicology headaches or bring up regulatory issues. The FDA, EMA, and similar health authorities demand strict documentation. Peptide chemists know trace amounts of side products or protecting-group remnants can sneak into the final product, affecting everything downstream.
One real-world example sticks out. My research group saw a promising new compound stall out with subpar animal data. Only after months of troubleshooting did a colleague track the problem to inconsistent purity between batches, traced back to a careless supplier. Switching to a source with tighter purity controls cleared up the problem, saving a year or more from being wasted.
Solutions in Today’s Chemical World
Nobody can just hope purity lands where it should. Regular sourcing audits make a difference. Scientists keep themselves out of trouble by running their own analytical tests—HPLC, NMR, sometimes even TLC for a quick check. It pays off to keep lines open with suppliers, demanding clear documentation and batch testing. Academic groups might share trusted suppliers across networks, knowing a single good reference is worth its weight in gold.
Automated platforms such as UPLC and MS give modern labs an edge. The chase for ever-higher standards is part of serious R&D, with major institutes now setting spectral libraries and digital logs for every batch. Students starting out quickly see the value—reactions that run clean with 99% pure Boc-(R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic Acid build trust in results, networks, manuscripts, and even careers.
Why Storage Matters
I’ve learned over the years that safe storage is often the step most skipped in handling products. Yet, the area where a product spends most of its life, whether that’s a warehouse, back room, or shelf, shapes everything from shelf life to quality to safety. If you ask anyone who’s lost money to product spoilage or recalls, they’ll probably point right at improper storage as the culprit. For food, medicine, electronics, or even paint, storage errors translate to waste, angry customers, and trouble with the law.
Temperature and Humidity: The Big Players
Take something simple like aspirin or a cream used in first aid kits. Most of us toss them in a cabinet and forget about them, until we see clumping, fading, or weird smells and colors. Too much heat or moisture is usually to blame. The FDA and Health Canada have laid out strict rules for these reasons: keep medicines in cool (usually 20–25°C), dry environments. Food takes the same road, though with specific twists for dairy, produce, or meats: cold storage below 4°C for perishables, tight seals to block out air, and dry bins for grains to stave off pests and mold. Electronics add their own layer, vulnerable to static, corrosion, and brittle parts when exposed to damp and fluctuating temperatures.
Contamination and Organization
A cluttered shelf or open bag might not seem like much until you’ve run into contamination that ruins entire batches. A company I worked for once left cleaning supplies near flour—no major spill, but odor seeped in and ruined the whole lot. Separation saves time and money. Hazardous products stay away from foods. Life-saving medicines get locked away from chemicals. Labeling isn’t just bureaucracy—clear tags help people avoid costly mix-ups and speed up recalls or stock checks. The World Health Organization publishes clear product categories and storage zones for a reason: accidents pile up fast in chaotic storerooms.
Shelf Life and Rotation
Ever forget about the milk at the back of the fridge? Businesses scale up that same issue, causing losses measured in thousands of dollars. Hospitals and distributors avoid this using FIFO (First In, First Out) principles. I’ve spent time in logistics, and without regular rotation and proper tracking, expiration dates sneak up, and outdated goods end up in customers’ hands. That opens up risk for lawsuits or damaged trust that takes years to rebuild. Good records and shelf design, with older stock in front, create real savings over the long run.
Security, Access, and Compliance
Theft and tampering come up more than you’d think, especially for high-value or sensitive products. Keeping lines of sight open, limiting who handles certain goods, and tracking every batch—these steps enforce compliance and peace of mind. In pharmaceuticals, this isn’t just good practice but a legal requirement, enforced by inspections from agencies like the FDA or EU authorities. Fines, recalls, and brand damage follow poor controls. Even in food businesses or electronics, product recalls trace back to gaps in handling or lax oversight during storage. Plain locks, logbooks, and regular audits might seem old school but still work well.
Better Storage Solutions
Not every business can afford fancy climate controls or automated inventory systems. Still, even basic steps—using pallets to keep stuff off damp floors, sealing lids on bins or bottles, training staff on handling and keeping up regular sweeps—make a huge difference. Talking to your suppliers, checking guidelines from public health or food safety authorities, and running frequent temperature checks cut risk and lift product quality.
Storage shapes the fate of every product. It protects investments, health, and sometimes even lives. Good practices pay for themselves, in both smoother daily work and in trust built with each safe, high-quality product in a customer’s hands.
Consumers Don’t All Think Alike
Walking down any grocery aisle, I notice how shelf space bursts with options, not just in brands, but in package sizes. From three-ounce coffee samplers to value bags stretching past my elbow, choice matters. Shoppers know life runs smoother when they can match what they buy to how they use it. A single student doesn’t fill a cart the same way a family with two teens does. My own college days called for tiny jars that fit in a dorm fridge; my life now swings closer to bulk packs. Everybody hits different rhythms and needs in their week. One-size-fits-all ignores that basic reality.
Waste and Wallets—Why Size Shapes Both
Many skip right over the impact packaging has on waste. Oversized boxes and bottles tempt with savings, but single folks often throw out spoiled goods. Buying more than needed hits landfills harder. A 2023 EPA report showed U.S. food waste approached 38 million tons per year. Much of that comes from packages just too large. That’s food, money, and environmental hope, all tossed out. Smaller sizes help cut down trash—less expired yogurt in the bin, less plastic covering our rivers.
Size determines cost savings, too. Bulk options usually carry a lower cost per ounce, but not everyone can spare that upfront price. People living on a strict monthly budget need the freedom to buy just enough—no more, no less. During a tight patch, I grabbed single-use packets instead of family-size tubs. Paycheck to paycheck, smaller units kept the fridge full without overdraft fees.
Product Safety and Accessibility
Package size decisions tie back to how safely people store and use products. Pills and cleaning sprays in large bottles mean more risk around kids. Tiny hands grab what they can reach. Regulations in countries like Canada and Germany already push for design changes—think childproof caps and warning labels—to fit package size. Retailers lose sleep over recalls caused by accidental ingestion. Smaller units carry less risk per container, keeping families safer.
Accessibility also comes into play. Folks with limited hand strength or eyesight need manageable containers. Gripping a gallon jug or reading a crowded label on a family-size bag feels impossible for many. Offering diverse sizes lets people choose what their bodies handle best. Last year, my grandmother switched brands because her preferred product stopped offering half-pint options; there just wasn’t a way for her to manage larger ones comfortably.
Business Responsibility—Skipping the Cookie Cutter
Brands often fall into a pattern, pushing their most profitable size and hoping shoppers adjust. Yet success stories come from companies listening closely. In 2022, a major detergent brand saw demand rise when it offered pods in several sizes, winning over both big households and single renters. Convenience stores thrive by selling smaller packages at a premium, catering to commuters needing “just enough.”
Retailers and manufacturers hold the keys. They can open the door to choice by observing local habits, gathering feedback, and adjusting quickly. A simple product survey, or even a glance at which sizes fly off shelves, gives clues that can lead to the next bestseller. “Is it available in different package sizes?” shows up everywhere because people crave choice. They want control over their spending, their routine, and what ends up in their trash can.
Better Packaging, Better Lives
Offering real size choices isn’t about cluttering shelves. It’s about respect—for people’s budgets, their space, their health, and the planet. Listening and responding to what people actually need has always delivered the most loyal customers. Brands and retailers stand to gain by moving beyond a single mold. The world thrives on variety—not just in flavor or color, but in every side of the shopping experience.
Medicine: Essential Roles in Modern Treatment
Most people encounter this compound at the pharmacy. Doctors prescribe medications that rely on it to control infections or ease pain. This compound often forms the backbone of antibiotics like amoxicillin and some over-the-counter painkillers. Hospitals use it daily for its quick action and dependable track record, and parents trust it for treating their kids’ stubborn fevers. Decades of successful outcomes make it a standard tool for keeping communities healthy.
Food and Beverage: Keeping Food Safe and Fresh
Many food manufacturers turn to this compound to keep their products safe on the shelves. In my years working around food safety, I’ve seen how it extends the life of meats, cheeses, and canned goods. Chemists discovered long ago that it acts as a barrier against spoilage, helping families avoid illness from bad food. Its familiar name can be found on the packaging of items ranging from pickles to sports drinks.
Agriculture: Building Healthy Crops
Ask any farmer, and they’ll tell you: healthy crops depend on more than just water and sunshine. This compound gives plants extra protection against pests and diseases. By adding it to fertilizers and sprays, growers reduce crop loss and fill markets with enough vegetables to meet demand. Regulators keep a close eye on how much lands in the soil, and advances in science make its use more targeted each year.
Cleaning Products: Powering Better Hygiene
Homeowners trust cleaning sprays and detergents that list this chemical as an ingredient. Its ability to break down grime and kill bacteria helps keep kitchens and bathrooms safe. Early on in the COVID-19 pandemic, shelves emptied of anything containing this compound, as people scrambled to disinfect surfaces. For many, it remains an unseen hero in the fight against illness.
Industrial Manufacturing: Building Blocks for Progress
Factories rely on this compound to create plastics, textiles, and paints. In my experience touring manufacturing plants, production lines grind to a halt without steady shipments. Technicians often mention it as the secret behind smooth coatings and bright colors. While it comes with environmental challenges, its role supports economies and everyday conveniences.
Potential Solutions for Safer Use
Dependence on this compound creates challenges, especially when overuse harms our water, soil, or bodies. Researchers work on safer alternatives and improved recycling. Careful labeling and tighter regulations can protect those most at risk, such as children or people with allergies. Consumers play a part, too: reading labels and choosing products that limit unnecessary exposure helps reduce the footprint.
Looking Ahead
Like salt or sugar, this compound touches many corners of modern life. From my own kitchen cabinet to the local hospital, it’s impossible to ignore its reach. Awareness and smart choices remain key as we keep searching for ways to balance its benefits with a healthier future.
What a COA Tells You
Asking for a Certificate of Analysis might sound like extra paperwork, but it cuts straight to the heart of trust and transparency. This document isn’t a fancy marketing brochure. It offers a window into the reality of what’s inside the product. If you’re buying supplements, chemical ingredients, or even food products, the COA becomes your proof. It lays out safety, purity, and whether the claims on the label stand up to lab scrutiny.
Real Experience With COAs
I remember working with a small supplement brand that prided itself on using "clean ingredients." Their customers started asking for COAs. At first, leadership thought this would be a hassle. The process pushed them to double-check the labs they used, confirm real batch testing, and look deeper at the supply chain. Not every batch lived up to the hype. This led to recalls, but also a stronger business. Trust grew. Sales followed. In my own life, I’ve seen friends waste money on products that later turned out to be counterfeit or contaminated. One batch of protein powder gave a neighbor a bad allergic reaction. The company had no COA—there was no answer when he asked what went wrong. It’s not just words on paper; it carries real weight for people’s health.
How COAs Build Confidence
Regulators like the FDA and industry groups use COAs as a baseline. They don’t stand in for every safeguard, but they help weed out products that cut corners. If a company hesitates or refuses to provide these certificates, it raises a red flag. Honest manufacturers don’t hide their results or testing methods. They use outside labs, check for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and put their name on it. The COA is like a report card anyone can read.
COA Isn’t Just for Experts
Some people hear “certificate of analysis” and picture something difficult to understand. In truth, most include straightforward details: batch numbers, passing/failing marks, and measured quantities for key ingredients. It’s not only chemists who gain from reading one. Anyone buying for a business, a pharmacy, or their home deserves clear, upfront details. Don’t fall for empty claims. With so many choices in the market, consumers need real facts. The COA puts power in anyone’s hands, not just industry insiders.
Solutions and What to Ask For
Stop settling for vague answers about quality. Demand COAs up front. Take time to read them. If you don’t understand something, ask about it—whether you’re dealing with a nutrition company, a cosmetics supplier, or an industrial vendor. If a product harms people, or if a batch gets pulled from shelves, the absence of a COA only makes things worse. Real companies welcome these questions, learn from mistakes, and invest in safer practices. When customers ask for proof, and companies deliver, everyone benefits.
The Path Ahead
Looking for a COA isn’t just for big corporations or scientists. It’s a habit that keeps businesses honest and families safe. The next time you buy something that could affect your health or safety, don’t shy away from this request. Every product that comes with a COA is one step closer to a market that values truth over empty guarantees.