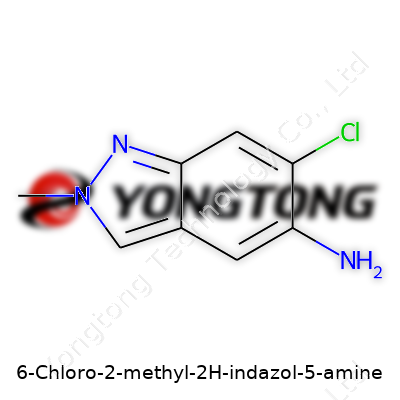
6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine: A Comprehensive Look
Historical Development
Exploring the history of 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine pulls back the curtain on the way chemical innovation often takes shape: a mix of necessity, curiosity, and practical stumbling forward. Researchers in the pharmaceutical arena first carved a path toward this compound out of an interest in indazole scaffolds, those versatile rings that play so nicely in drug design and agrochemical chemistry. Back in the late 20th century, new methods for selective chlorination and methylation made it feasible to modify indazole rings in ways that weren’t possible before. Lab journals from the 1990s document tweaks in reaction temperature and solvent choice, an approach fueled by a real drive to find molecules that could act as building blocks for kinase inhibitors, anti-inflammatory drugs, and fungicides alike. In my early research days poring over hand-written synthetic notes, it struck me how tangible and trial-and-error the field could be — and how each variant like 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine appeared as both an achievement and a springboard for the next question.
Product Overview
6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine stands out as a small organic compound built around the indazole ring, with chlorine and methyl groups bringing targeted changes in reactivity and selectivity. Chemists reach for this product in part because its amine group at the 5-position offers a direct handle for further functionalization — amidation, sulfonylation, and a stack of other transformations flow from here. The structure’s backbone supports studies beyond medicinal chemistry, stretching into materials research and chemical biology. As someone who’s handled a range of specialty heterocycles, it’s easy to appreciate how a well-placed substituent like a chloro or methyl group changes the fate of a molecule in a reaction round in sometimes dramatic ways. Lab companies offer this compound in curated purity grades, tailored to synth work — not for casual tinkering in basement setups.
Physical & Chemical Properties
The physical form typically appears as a white to pale yellow crystalline solid, with a melting point commonly in the 180–200°C range, though purity and processing can nudge that number. Crystals handle reasonably well under glovebox conditions, but open-air storage brings some risk of slow discoloration if moisture or light persist. Solubility hovers moderate in polar organics like dimethyl sulfoxide or N,N-dimethylformamide, with far lower tendencies to dissolve in straight water. The compound’s chlorine and methyl substitutions tweak electron density around the ring, affecting both stability and reactivity. NMR spectra sing with distinct downfield signals reflecting the aromatic protons, while mass spectrometry confirms the expected molecular ion, helping to head off confusion with similar analogues. Stability under room temperature remains solid for short-term experiments, though it pays to keep supplies sealed and tucked away from heat sources.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Purity and identity confirm the starting point for research success. Reliable vendors list the purity at greater than 97%, with residual solvent levels, heavy metals, and water content typically measured and reported on the certificate of analysis. Flammable solid warnings and the standard GHS pictograms draw the eye on the product label, and safety data sheets bluntly spell out risks. The label details batch number, synthesis date, and recommended storage conditions — usually in a cool, dry place, with desiccant included. From the perspective of hands-on lab work, spotting these details in advance lets the researcher focus on the chemistry, not on uncertainties about the material at hand. Documentation still matters more in regulated labs, where audit trails get as much scrutiny as final assay results.
Preparation Method
Synthesis kicks off with a suitable indazole precursor. Selective chlorination, about as fun as it sounds, places a chlorine atom at the 6-position, using reagents like N-chlorosuccinimide in anhydrous conditions. Methylation at the 2-position may follow through Grignard or alkylation strategies depending on precursor availability, and amination finishes the job, either by direct nucleophilic substitution or from reducing a nitro precursor at position five. Process chemists optimize yield by balancing temperature, reaction time, and solvent choice, cycling through rounds of adjusting conditions to prevent over-chlorination or side reactions. Purification usually leans on recrystallization or column chromatography, and all steps require a steady logistical hand, thoughtful about both risk and environmental footprint. Tracking every step in the synthetic route, down to reagent batch and quench timing, builds traceability — a hard lesson learned after a batch ruined due to an overlooked bottle switch in my early days.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine isn’t just an endpoint compound — it’s a reactive partner in a variety of chemistries. The amine group invites acylations and sulfonylations for library expansion, and coupling partners with isocyanates, aldehydes, or sulfonyl chlorides yield a spectrum of derivatives with distinct biological or physical properties. The chlorine atom, sitting as an electron-withdrawing group, directs metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions like Suzuki or Buchwald–Hartwig, essential for medicinal chemistry programs searching for active analogs. My time working in a medicinal chemistry core saw this molecule serve as a backbone for kinase inhibitor candidates, with fluorination, alkoxylation, and aryl-boron additions coming in rapid cycles as structure-activity relationships took shape. Chemists appreciate the way this indazole opens doors for small tweaks, allowing for rapid scaffolding into new chemical space.
Synonyms & Product Names
This molecule doesn’t travel under just one name. Aside from 6-chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine, catalogs call it 6-chloro-2-methyl-indazol-5-amine and 5-amino-6-chloro-2-methylindazole. Some product lists drop the hydrogen, listing it as 2-methyl-6-chloroindazol-5-amine. Whether someone uses a local lab code or a product catalog number, those in the know recognize it as a core substituted indazole. Chemistry communication leans on CAS numbers to avoid missteps, as synonyms lead to mix-ups, especially for those new to the field or unfamiliar with the naming conventions that crop up region-to-region in the literature and markets alike.
Safety & Operational Standards
Direct contact with 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine poses risks common to many organic amines and indazole derivatives. Inhalation or skin exposure may trigger irritation, and eye contact warrants particular caution. Lab practice expects gloves, splash goggles, and a well-ventilated fume hood during weighing or transfers. Disposal routes follow organic waste streams, keeping the compound away from drains or regular trash. Emergency showers and eyewash stations should be within arm’s reach anywhere synthesis or handling happens. Documentation drills keep staff aware of hazards, and training schedules ensure updated responses for spills or exposures — a routine that pays off when a dropped vial turns a regular afternoon into a safety review in real time. Lab managers balance speed with discipline, knowing that short-cutting protocols lands teams in trouble far faster than anyone expects in the rush of a busy day.
Application Area
Pharmaceutical and agrochemical firms draw on 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine as an early-stage intermediate for bioactive molecule synthesis. Drug discovery often turns to substituted indazoles for kinase inhibitors or neuroactive modulators, and this compound’s functional groups give medicinal chemists room to build and alter activity profiles. Crop science labs evaluate derivatives as potential fungicides and herbicides, measuring both efficacy and environmental persistence. In academic circles, the molecule provides a test case for mechanistic organic chemistry studies, where reactivity patterns of substituted indazoles map onto new reaction conditions or catalyst design. For anyone who’s tried to move from milligrams to grams in a scale-up, the compound’s reproducible synthesis and clear reactivity make it a workhorse for both bench-scale and pilot-scale experiments.
Research & Development
Current research pushes at the boundaries of indazole chemistry: new synthesis routes, catalyst-driven functionalizations, and applications in increasingly specialized biological screens. Multi-step syntheses keep tightening their green credentials, swapping hazardous solvents for safe alternatives and dropping energy use with microwave or flow-chemistry setups. Biological evaluation, driven by the hope of unearthing new activities, uses compound libraries populated by small changes around the indazole core. Automated screening platforms, combined with machine learning, now help predict promising modifications, a far cry from the all-manual screening rounds that once dominated. Throughout these efforts, the lessons from each failed run steer adjustments for the next synthesis, feeding back not just into that one project, but into every compound based on that core structure.
Toxicity Research
Every compound finds its future defined, at least in part, by its hazards. Preliminary toxicology data for 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine suggests moderate acute toxicity, with careful dose assessment required for animal studies or biological screens. Chronic effects, reproductive risks, and breakdown product profiles often remain sketchier due to the compound’s intermediate status — not yet a marketed drug or consumer product, but a tool in the toolkit for those developing such end products. Labs log exposures meticulously, supporting downstream studies on environmental persistence, metabolic fates, and safety pharmacology. Risk assessment frameworks, built around real toxicology readings rather than just theoretical prediction, remind everyone on the team that innovation and caution walk hand in hand, especially with bioactive scaffolds like indazoles.
Future Prospects
Interest in 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine is only set to grow as chemical space continues to expand. Machine learning and automated retrosynthesis tools accelerate the discovery of new derivatives, and improved safety testing helps steer these molecules into commercial pipelines more quickly than ever before. Process intensification through flow reactors or microwave helps streamline access, making it easier for chemists to integrate this building block into early phase medicinal and material science projects. Regulatory engagement will drive further disclosure on safety, impurity control, and supply chain assurance — an outcome that benefits everyone in the long run. For those of us who saw indazoles as mere curiosities on a reagent shelf, it’s satisfying to watch this molecule become a staple ingredient in the next generation of research-driven solutions to society’s needs.
Understanding the Chemistry of the Compound
6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine has a chemical structure rooted in a classic indazole ring. For anyone delving into the details, the indazole core contains a bicyclic system with two fused rings—one benzene and one pyrazole. This might sound like jargon, but here’s what matters: chemists see the indazole nucleus as a stable, versatile building block. Once a chlorine atom attaches at the sixth carbon, and a methyl group tacks onto the second position, things get interesting. The amine group landing on the fifth carbon gives the molecule its unique behavior.
Why This Structure Matters
Chlorinated indazoles stand out in medicinal chemistry. Adding a chlorine atom often makes a compound more resistant to enzymes that break down molecules in the body. This means drugs crafted with structures like 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine can last longer and keep their therapeutic effect stable. The methyl group on the second carbon brings lipophilicity—the molecule dissolves in fats better. In drug design, this allows easier travel through cell membranes, potentially delivering a stronger action. The amine group opens doors for bonding, making the molecule reactive and letting scientists attach different side chains or functional groups to experiment with new treatments.
Drawing the Structure: A Simple Visual Guide
To see it in your mind’s eye, picture the indazole’s two rings fused together. A chlorine atom pops out from one of the rings (the sixth carbon spot), a tiny methyl group sticks out at the second position, and a lone amine group (NH2) decorates the fifth carbon. The chemical formula looks like this: C8H8ClN3. Chemists use the SMILES notation for digital modeling: Cc1[nH]nc2cc(N)cc(Cl)c12. With these markers, software (and people) can generate 3D models to play with the possibilities.
Potential and Limitations
Research teams chase after cores like 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine because indazole derivatives show activity against cancers, infections, and inflammation. Chlorine and methyl groups often bump up the bioavailability of these types of molecules. That boosts the interest from both pharmaceutical companies and academic labs. Even so, chlorine atoms don’t always play nice. Sometimes they make compounds more toxic or harder for the body to digest safely. Finding the right balance between effectiveness and safety shapes much of this research.
Responsible Use and Next Steps
New molecules can change medicine for the better, but that promise comes with big responsibility. Lab safety should never take a back seat. Scientists handling and modifying 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine run toxicity studies as early as possible, using in silico models to flag dangerous properties before bringing compounds near animals or people. Environmental safety counts, too. Chlorinated compounds can sometimes linger in soil or water, so a green chemistry approach matters. Using less hazardous reagents and searching for biodegradable alternatives can help lower risks as researchers push forward. In my own experience, the most interesting discoveries come from a blend of excitement and caution. The structure of 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine opens doors—the best outcomes come when every new step keeps ethics, safety, and sustainability in mind.
What Sets This Compound Apart
6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine doesn’t turn heads in the way everyday drugs or household chemicals do, but it helps shape important innovations. I’ve worked in chemical research labs, and I know firsthand how the right building block can open doors in drug discovery or material science. This compound, built around the sturdy indazole core, shows unique promise thanks to its chlorine and amine groups. These features make it more than just another reagent sitting on a shelf. Like many researchers, I’ve learned to keep an eye on molecules like this—simple on paper, but packed with potential.
Pharmaceutical Research: More Than Just an Intermediate
Medicinal chemists often search for starting materials to build new drug candidates. I’ve seen projects stall until the right scaffold shows up. Here, 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine finds its place. Its chemical structure offers fertile ground for tweaks and substitutions, which is essential for tuning biological activity. Drug companies have tapped into indazole-based molecules to design agents against cancer, inflammation, and infectious diseases. The chlorine atom on this compound often improves drug-like behavior by changing how it interacts with biological systems. The amine group, on the other hand, allows connections to new chemical groups that could improve potency or lower toxicity. I’ve seen a few labs push compounds like this further, chasing unexpected results—a big reason innovation happens in medicine.
A Foot in the Door of Agrochemicals
Crop protection runs on chemistry. Many common herbicides and fungicides use heterocyclic backbones. Chemists in the agricultural field value indazole derivatives for their ability to disrupt pests in targeted ways. By bringing this compound into the mix, developers can screen a range of related molecules. Farms benefit from newer, safer, and more effective products. One small change—like swapping in a chlorine atom—sometimes turns a dud into a breakthrough. Years ago, I watched a team test dozens of variations before one molecule met strict environmental and safety standards. A flexible compound like this can give such projects a running start.
Shaping Dye and Material Science
Some chemists use this molecule in specialty dyes and pigments. Strong chromophores rely on stable, nitrogen-based rings, which the indazole group supplies. Substituted amines and chlorinated rings add deeper color, higher stability, and resistance to fading. In textile or ink manufacturing, stronger colorfastness and less leaching mean longer-lasting products and less waste. Eco-friendlier approaches stand out more today: chemists look for dye precursors that break down cleanly, and this indazole variant fits the bill better than older, dirtier options.
Moving Toward Greener Production
Manufacturing the compound can raise safety or environmental questions. Responsible companies search for routes that avoid hazardous by-products. Where I’ve worked, we cut down hazardous waste by using milder reagents and finding better purification steps. Modern labs track every solvent and by-product, aiming for cleaner syntheses with each run. Sharing these lessons helps smaller shops and researchers keep up. Through persistent effort, safer methods and improved recycling will shrink the impact over time and keep workers safe while producing the materials modern industries demand.
Why Purity Sets the Stage
Every time I see a new batch of a chemical compound roll into a lab, my first impulse is to check its certificate of analysis. Purity isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity if you want chemistry that works. In pharmaceutical research, for example, even a one-percent impurity can turn an otherwise promising drug candidate into a failed experiment. R&D work grinds to a halt if the building blocks don’t meet expectations. Scientists have learned this lesson the hard way, facing ruined trials and questionable data due to unnoticed contaminants.
Manufacturers use techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to screen out anything but the compound of interest. Analytical data doesn’t just reassure chemists; it points to safe products for the end user. In food additives and nutritional supplements, purity means the difference between a safe ingredient and a regulatory headache. No one wants to see recalls or health alerts caused by slack quality standards.
Looks Speak Volumes
Physical appearance might sound cosmetic, but it tells a story about what’s inside the bottle. A compound, pure in theory, should match its expected visual traits. A white crystalline powder shows up on a product sheet, and that’s what smart buyers demand in real shipments. Off-color spots, clumps, or a strange odor hint at problems—bad storage, moisture, contact with air, or something more sinister. Each physical detail, from color to consistency, flags up skips in production or shipping.
I still remember the shock in a colleague’s voice after opening a container and finding a yellowish tinge where only white crystals belonged. That shipment got pulled immediately, and later testing pinned the issue down to trace metals from an old manufacturing line. Physical inspection—simple as it sounds—can prevent a company from risking its reputation and customer trust.
The Link to Trust and Results
End users trust the testing because they know a slip-up means setbacks, wasted money, or worse. Reputable suppliers routinely update their analytical protocols, share detailed spectroscopic graphs, and back up batches with transparent documentation. This kind of openness builds trust from pharmaceutical giants to backyard soap-makers. If a supplier hesitates to provide purity data or ignores questions about color or texture, it’s time to look elsewhere.
For industries that touch health, safety, or tech, mistakes hurt more than bottom lines. Take semiconductors as an example; trace contaminants—undetectable without rigorous checks—can destroy a whole chip batch worth thousands of dollars. In this space, every part of the process, from synthesis to storage, receives close attention. Purity details don't just float in regulatory paperwork; they stop disasters before they start.
Raising the Bar
Insisting on certifications, transparent data, and regular audits helps keep grey-market suppliers off the table. Quick visual checks and reliable lab reports keep everyone honest. If a compound’s appearance doesn’t match expectations, or the numbers don’t line up, refusing the material is the only smart move.
Industry doesn’t reward shortcuts. Paying attention to purity and appearance creates a system where mistakes get caught early, products perform as promised, and everyone sleeps better knowing they’ve put the right stuff to use.
Safety Starts Before Opening the Bottle
Every researcher or lab tech who works with chemicals knows the story: one slipup with storage, and a lot of precious material—and time—gets wasted. 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine doesn’t care about intentions; it just follows chemistry. The white-to-off-white powder holds its properties best under the right conditions. From experience, ignoring manufacturer guidelines or scientific literature can mean hard lessons.
Temperature
Below room temperature is the recommendation for storage, usually around 2–8°C. This simple move limits risk. Warmer spaces can trigger slow decomposition or promote moisture uptake. Even if the powder looks unchanged, impurities and degraded fragments might sneak in, throwing off purity or studies. Lab benches may be convenient, but refrigerators win for long-term reliability.
Container and Sealing
Moisture creeps in faster than many think. A tightly closed, screw-capped glass container, preferably amber to block light, guards against air and humidity. Plastic jars may work for short periods, but certain plastics let tiny molecules in over time. After handling, a dry scoop or spatula keeps water out. Joining separate containers or letting the jar sit open in the air brings risk of clumping, loss of potency, or unpredictable reactions.
Moisture and Light
Desiccators with silica gel or other desiccants provide real value. Humid environments—especially in the rainy season—cause powders to cake or degrade. Desiccation extends shelf life and saves repeat purchases. Light can also play tricks on compounds like this, sometimes causing color changes or breakdown. Transferring the powder into a clear jar for convenience is tempting, but the cost in stability often outweighs the small benefit.
Labeling and Record-keeping
Without sharp labels, mistakes pile up. Dates of receipt, container opening, and weighing should be tracked. I’ve seen too many refrigerators full of mysterious powders or misremembered samples. Clean handwriting and digital records save confusion, especially in shared labs. Batch numbers, concentrations, and any warnings straight from the supplier stay visible for safety and traceability.
Disposal and Spills
Spills and waste sound minor, but many compounds related to indazoles need careful handling. Proper storage goes together with proper disposal. Absorbing spills with clean paper, collecting as hazardous waste, and avoiding drains make a foundation for both safety and legal compliance. Strong ventilation, gloves, lab coats, and goggles round out the protection.
Quality Control and Inspections
Periodic checks work well. Every few months, reviewing the chemical’s appearance and any data from analytical tests—melting point, NMR, HPLC—uncovers slow changes or error patterns. Stockrooms with set quotas for ordering and timelines for use prevent hoarding and loss through age or neglect.
Why It Matters
Labs depend on predictable outcomes. Controlling moisture, temperature, and light for chemicals like 6-Chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-amine helps protect research integrity, personal safety, and lab budgets. Sticking to tried-and-true practices based on real-world experience and science leads to fewer surprises and better science.
Why Handling This Product Isn’t Like Picking Up Groceries
Taking precautions goes beyond keeping a tidy workbench. Some products demand respect because a shortcut or missed glove can cost health or peace of mind. Certain ingredients, even with familiar names, might sting, irritate skin, or create dangerous fumes. Paying attention to the ways you store, pour, and even transport these materials makes a real difference. Nobody wants to lose days at work or face a hospital trip over something that only needed a splash of common sense and a pair of goggles.
What the Facts Tell Us
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention points out that much of workplace injury happens because people underestimate chemical exposure or ignore warnings. Burns, rashes, and long-term lung troubles add up in the data. Simple mistakes, like mixing incompatible substances or skipping a mask, sit behind most accidents. A 2020 report found that almost a quarter of chemical injuries occur because safe handling rules fell by the wayside. The same CDC report recommends looking at each product’s safety data, often tucked inside boxes or online. These sheets aren’t just paperwork—they’re packed with real examples of what happens if something spills, splashes in an eye, or turns to vapor.
Experience on the Worksite: It’s Not Just About You
Anyone who has spent time in a shop or lab knows someone who shrugged off a warning. Gloves get left behind, spills get wiped up with a sleeve, and open containers sit out longer than they should. From what I've seen, these little shortcuts pile up. The impact goes beyond the person who made the mistake. If someone stirs up dust or lets chemicals escape, others breathe it in or slip on the residue. Mistakes multiply in shared spaces. Safety demands team habits, not just locker-room pep talks.
Smart Habits at Every Step
Storing this product in a cool, dry spot, away from children and animals, always pays off. Original packaging matters. Those labels tell a story—expiration date, use by, flammable, corrosive, toxic. A sealed lid does more than prevent leaks; it keeps air and light out, protecting everyone from accidental exposure. Once you start working, gear comes into play. Gloves made for the task stop absorption through the skin. Splash-proof goggles protect your eyes. Sometimes, the right mask guards your lungs against dust or vapors that can linger even after the job ends.
Washing up after handling makes a difference. Some substances stick around longer than expected, so what feels like a small amount can cause problems if it travels into homes or cars. Rinse thoroughly, change clothes, and don’t forget to clean shared surfaces—even the floor, since powder or residue can get tracked around.
Getting Ready for the Unexpected
Accidents don’t run on a schedule. Keeping eyewash stations and spill kits within arm’s reach saves more time than regular sinks or paper towels. Quick response stops problems from spreading. Each place that handles this product should post instructions someplace obvious. The best run shops I’ve worked in make a habit of reviewing what to do in a pinch. It takes just a couple minutes a month, and those minutes count when things go wrong.
Looking Ahead: Staying Safe Means Staying Smart
Technology and regulations change, but the heart of safe handling remains steady. Read the label. Respect the product’s risks. Train the team. See safety as prevention, not reaction. Healthy habits now keep everyone ready for work tomorrow—and nobody gets left fixing a preventable mistake.