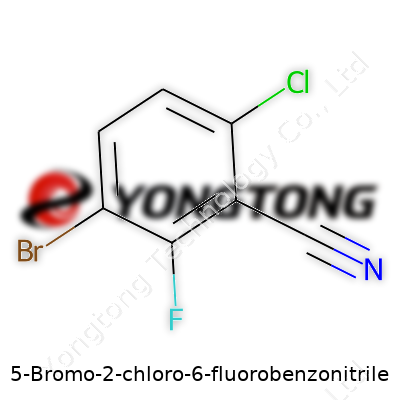
5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile: From History to Future
Tracing the Historical Roots
Chemistry never stands still. The search for better building blocks often leads to aryl halides, and 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile has found its niche in the broader context of aromatic chemistry. Looking back at the wave of organic synthesis in the twentieth century, research groups raced to unlock new intermediates for agricultural, pharmaceutical, and material advancements. It didn’t take long before halogen-substituted benzonitriles drew attention, given how halogens alter reactivity and introduce functionality at the bench. Years of incremental development sharpened routes to selective halogenation, and the compound became less of a specialty chemical and more of a workhorse for researchers aiming for reliable outcomes.
The Product at a Glance
This substance wears many hats in the lab. Officially labeled as 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile, it brings a trifecta of halogens onto a benzene ring with a nitrile group, forming a framework that enables unique transformations in synthesis. Academic labs and manufacturers use this compound to develop functional materials, explore pharmaceutical leads, and craft custom molecules that underpin crop protection or dye chemistry. Each lot that lands on my desk drives home just how essential fine-tuned reagents remain for practical progress in chemistry.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile usually appears as a pale solid, and the presence of three different halogens introduces subtle patterns in its melting point and solubility. Expect it to stand up well in storage, resisting moisture and light degradation due to the electron-withdrawing power of the substituents surrounding the core ring. Boiling and melting behavior sits at higher values compared to less substituted benzonitriles, offering ease of isolation. On the reactivity front, the combination of bromine, chlorine, and fluorine shapes selectivity for substitution reactions and cross-coupling applications, especially when aiming for regioisomer-safe products.
The Technical Details and Product Labeling
Every bottle arrives carefully labeled with a CAS number, purity exceeding 98%, and a warning about the hazards that come standard with aryl halides. Purity matters—a trace impurity can derail a research project. Moisture content, trace metal levels, and isomeric purity are tightly controlled, and manufacturers typically back up their specifications with HPLC and NMR profiles to give confidence to the end user. In my own experience, product traceability ranks high for those seeking reproducibility in their results, so transparent labeling and supply chain assurances make all the difference.
Methods of Preparation
Scaling up the synthesis of 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile relies on time-tested strategies from aromatic chemistry. Starting with a benzonitrile backbone, selective halogenation routes use organometallic intermediates or specialized halogenating agents. Success here depends on reaction temperature, solvent choice, and order of addition, as one misplaced halogen shifts outcome drastically. Industrial setups prioritize cost and safety, using batch or flow chemistry to control exotherms and minimize byproducts. This journey from bench to ton-scale delivers a compound sturdy enough for commercial use but versatile enough for academic pursuits.
Exploring Chemical Reactions & Modifications
The structure opens doors for custom chemistry—cross-coupling, nucleophilic aromatic substitution, or reduction reactions benefit from the distribution of halogens and the reactive nitrile. In making advanced intermediates or drug candidates, the selective removal or exchange of bromine and chlorine is a favorite tactic. The nitrile usually stays put, anchoring further elaboration. Researchers in my orbit appreciate the product's clean response to Suzuki or Buchwald–Hartwig coupling conditions, helping craft complex, functionalized molecules without detours or surprises.
Alternative Names and Product Listings
You’ll find this compound under several banners, such as 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile, 2-Chloro-5-bromo-6-fluorobenzonitrile, or by shorter trade codes in catalogues from major suppliers. Documentation using these alternatives keeps consistency across regulatory filings or patent applications. Recognizing these synonyms prevents costly mistakes in procurement or cross-border transactions.
Safety Standards and Operational Protocols
Handling halogenated benzonitriles calls for diligence. Proper gloves, goggles, and local ventilation go a long way toward preventing skin sensitization or inhalation issues. The compound doesn’t vaporize easily, but caution matters, especially in larger operations where dust or spill risks rise. Waste management procedures must follow established guidelines for halogenated organics—incineration or specialized treatment avoids buildup of persistent contaminants. Regular safety training builds a culture where incidents become rare, and chemical waste never becomes an afterthought.
Key Application Areas
5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile claims real utility across several industries. Agrochemical researchers pursue new pesticide leads using its scaffold for resistance management. Pharma finds it valuable in small molecule discovery, where selective substitution unlocks new mechanisms or bioactivity. Its structure also attracts interest from electronics chemists, who integrate it into materials for semiconductors or OLED devices. For academics, it delivers a reliable handle to probe reaction mechanisms or teach core concepts in aromatic substitution.
Developments in Research and Ongoing Innovation
The last decade brought fresh eyes to aryl halides, thanks to catalyst development and greener synthetic methods. Research into direct halogenation, milder cross-coupling, and automation pits efficiency against cost and sustainability targets. Big data and machine learning also enter the scene, predicting optimal conditions to turn this compound into more advanced products faster and with fewer steps. Watching labs publish on biorthogonal labeling or upcycling strategies gives a sense of how essential this intermediate has become, feeding directly into renewable chemistry ambitions.
Toxicity Research
Early studies hint at relatively low acute toxicity but give cause for caution with repeated exposure or in large environmental releases. Subtle chronic effects on liver and reproductive health push for diligent personal protection and strict containment. Regulatory agencies flag this class of chemicals for attention because bioaccumulation remains poorly characterized, particularly for highly substituted aromatics. Ongoing animal and cell line studies try to tease out thresholds for exposure, while environmental chemists monitor downstream impacts as aryl cyanides move through soil and water systems.
Outlook and Future Prospects
A chemical with this much versatility won’t fade from relevance any time soon. As synthetic pathways move toward automation and customization, demand grows for reliable building blocks that make complexity manageable. Companies investing in cleaner halogenation steps, lower-waste processes, and safer precursors strengthen the compound’s position in the toolkit. Trends in molecular electronics, sustainable pesticide development, and precision medicine point toward greater emphasis on halogenated scaffolds with defined reactivity—exactly where 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile shines. Building experience with it in real-world settings means problems get solved faster, and the next generation of chemists inherits a tool they trust.
Unraveling the Formula
Ask a chemist about 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile, and you’ll hear the answer: C7H2BrClFN. It looks dense on paper, but each letter and number tells a part of the story. At its core, this compound brings together a benzene ring, touched with a nitrile group—so that’s the benzonitrile. Then the ring wears three different halogen patches: a bromine at carbon 5, a chlorine at carbon 2, and a fluorine at carbon 6. Every one of these additions tweaks the molecule’s personality, making it valuable for chemistry labs and the industries that depend on precise molecular design.
Why This Formula Matters in Real Labs
I remember the first time I struggled to piece together formulas for substituted aromatic compounds. All the halogens compete for space in the ring, and one wrong placement turns the substance into something completely different. Think of C7H2BrClFN as a blueprint for a tool that helps researchers build more complex molecules. In pharmaceutical labs, swapping halogens on aromatic rings helps drug makers optimize everything from stability to how drugs interact with the body.
Slight modifications in these formulas often spell the difference between a breakthrough and a dud. For example, putting bromine, chlorine, and fluorine all together on the same ring changes how the molecule dissolves, how it binds with proteins, and even how long it hangs around in the environment.
Challenges in Synthesis and Safety
Working with compounds like 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile doesn’t just mean scribbling formulas—it means getting your hands dirty with the right reactions and being careful about safety. Halogens such as bromine and chlorine require careful handling, not only for the chemist’s health but also for the planet. Waste from these reactions can linger in waterways, affecting plants and animals. In the lab, nitriles present another concern, since some release toxic gases during synthesis or breakdown.
Over the years, more labs have turned to greener chemistry, cutting down on solvents and hazardous reagents. For example, microwaves now help speed up reactions, using less energy and generating less waste. Other teams have found catalysts that use less metal or produce fewer unwanted by-products. It takes a lot of trial and error—no shortcut replaces care and good data.
What Industry and Academia Can Do
Scaling up means looking out for both efficiency and the community. One solution: closed-loop production systems that recycle halogenated waste instead of dumping it. Universities and companies often invest in research to find alternative synthesis pathways, sometimes using enzymes to add or shuffle halogen atoms. In my time volunteering at an academic lab, the best progress came from regular conversations with environmental scientists, engineers, and process chemists—bringing all hands on deck to keep new compounds safe and sustainable.
Chemical formulas don’t exist in a vacuum. Each new structure brings opportunities to treat illness, build materials, or solve problems. But the responsibility follows. By keeping a sharp eye on every atom—from formula to finished product—chemists protect more than just test tubes. They look out for workers, neighbors, and future generations.
Why Industry Cares About This Compound
Anyone who has wandered through a chemical laboratory probably recognizes that odd mix of caution and excitement when a substance with multiple halogens shows up on the shelf. 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile sits in that camp. The moment those three halogen atoms and a nitrile pop up on the same benzene ring, chemists start thinking about possibilities—in pharmaceuticals, crop science, and beyond.
Drug development often feels like a race against time. New diseases, new resistance patterns, and evolving patient needs force scientists to search for new building blocks every year. This compound, with its peculiar fingerprint, acts as a foundation stone in synthesizing more complex molecules. Medicinal chemists turn to it as a starting material for the scaffolds of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). For example, fluorine atoms help drugs linger in the body longer, bromine tunes potency, and a nitrile group helps form diverse molecular shapes. The appeal comes from direct experience: building molecules for new drugs gets easier when you start with a versatile, highly reactive aromatic like this one.
What It Means for Agriculture and Crop Science
Farmers and global food chains keep looking for ways to increase yields and fend off pests. Crop protection scientists borrow tactics from drug discovery—start with a promising molecule and add or subtract functional groups until something useful appears. This benzonitrile fits the bill for structural diversity. Its unique substitution pattern lets researchers attach it to other functional groups, creating pesticides, herbicides, or fungicides with new modes of action. In my work with agrochemical projects, we constantly test dozens of new candidates every season, and molecules like this usually pass through early screening because the halogens encourage targeted activity while holding back toxicity.
The Materials Connection
Outside health and agriculture, specialty chemicals make life smoother, from semiconductors to next-gen polymers. 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile occasionally enters the ring here too. Chemists use it to craft liquid crystals, which display information across flat screens, or as tools to design new dyes and pigments. In polymer labs, I’ve seen folks leverage its mix of electron-withdrawing groups to tune the stability and flame resistance of finished materials, translating niche chemistry into products we ignore, yet rely on, every day.
Supply, Regulations, and Smart Handling
Trouble rarely knocks on the front door in a chemistry lab. But potent halogenated compounds demand respect. Environmental agencies around the world, from the US EPA to the European Chemicals Agency, lay out detailed guidance for safe production, usage, and disposal. In the labs where I’ve worked, strict labeling and robust waste management stopped accidents before they started. Commercial suppliers meet increasing expectations—traceability, purity, ethical sourcing—before vials leave the warehouse.
Looking Toward Safer and Greener Chemistry
Whether pushing boundaries in medicine, farming, or electronics, every chemist I know keeps one eye on sustainability. Handling and making molecules like 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile responsibly matters as much as harnessing its benefits. Switching to greener solvents, investing in recycling systems for waste halogens, and treating emissions as priorities—these keep labs not only busy, but safe and trusted by their neighbors.
A Chemical That Demands Respect
5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile finds use in advanced pharmaceutical and specialty chemical synthesis. Over the years, I’ve handled several halogenated benzonitriles, and their risks stay pretty consistent: strong odors, potential for skin and eye irritation, and toxic fumes when heated or burned. Any lab or warehouse that deals with such compounds needs a plan grounded in real safety habits, not just paperwork.
Staying Ahead with Smart Storage Choices
This chemical holds up best in cool, dry storage. Direct sunlight speeds up degradation and may even trigger unwanted byproducts that bring more hazards. I always trust thick-walled amber glass bottles with airtight PTFE-lined caps for such reactive organics. You want labeling that emphasizes the halogens and the nitrile group—those parts drive the biggest risks. Neat, legible, and chemical-resistant labels prevent dangerous mix-ups.
Keep it off high shelves. If you reach up and a bottle slips, the clean-up gets complicated and exposure risk spikes. In my old lab, we set a rule: halogenated nitriles only on mid-level shelves with spill trays underneath. Use separate flammables cabinets distinct from oxidizers or acids. Moisture spells trouble, so skip fridges with condensation problems and avoid rooms with high humidity. Desiccators with reliably fresh silica gel help, especially if you’re storing open bottles between uses.
Personal Safety: No Shortcuts
I’ve seen even seasoned chemists underestimate these substances. Basic nitriles sting with a whiff; toss in halogens and you’re handling complex toxicology. Always wear chemical splash goggles, gloves made from nitrile or butyl rubber, and a solid lab coat. For big transfers, full face shields and chemical-resistant aprons become necessary. You can’t predict spills or splashes, so preloading the habit makes all the difference.
Ventilation proves crucial. Work in a certified fume hood, not an open benchtop. The nitrile group releases poisonous gases if the compound heats up or catches fire, and fumes seep out even without visible smoke. Never rely on building air circulation—it’s just not meant for this job.
Managing Spills and Waste Responsibly
Industrial practice taught me that accidents seldom warn in advance. Spill cleanup kits with absorbent pads labeled for halogenated organics belong right near where you open the bottle. Staff should rehearse cleanup protocols, including personal decontamination and proper notification channels. Double-bag all cleanup materials and spent gloves in labeled hazardous waste drums. Treat broken glassware as both chemical and physical hazard.
Disposal of leftover material goes to specialty hazardous waste contractors. Flushing even milligram amounts down the sink fails both safety and environmental standards—besides being illegal in many regions. Contact local regulatory agencies for requirements: halogenated organics land on nearly every “do not pour” list worldwide due to persistence and toxic breakdown products.
Good Habits, Not Just Regulations
Manufacturers design SDS sheets for compliance, but safety culture sticks through real training and honest reminders. I see the difference in labs where workers double-check each other, update storage records, and review procedures after near-misses. 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile doesn’t forgive small mistakes—the stakes demand commitment from everyone who handles or stores it. In the end, what saves the day isn’t the text of a rulebook, but the practical wisdom built from careful observation and open communication among the crew.
The Value Behind Purity in Fine Chemicals
In the world of fine chemicals, finding a reliable grade for a compound like 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile feels like a real test of patience. Every chemist and manufacturer knows purity isn’t just a number printed on a spec sheet—it shapes results, impacts safety, and controls the bottom line in every batch produced. Most suppliers advertise purity at or above 98%, with the leading catalogs sometimes promising more than 99%. HPLC, NMR, GC, and MS analyses generally back up these claims, but actual performance tells the truest story. Tiny contaminants can spark headaches in any downstream synthesis or pharmaceutical intermediate.
Specification Sheets: Not Just Paperwork
Specification sheets, usually issued by large chemical houses or trusted distributors, spell out the proof. Typical specs for this compound include detailed limits on water content (using Karl Fischer titration), clarity over single versus mixed isomer presence, and levels of trace metals or solvent residues. Knowledgeable buyers double-check that metals like iron, palladium, and copper remain controlled, especially when looking at compounds used for pharma or high-value materials. From hands-on experience, asking for the trace impurity profile proves to be a smart first move, especially when quality standards tighten year after year. Even seasoned research veterans have seen promising reactions derailed due to ignored minor impurities.
Why Purity Matters—Beyond the Lab
Imagine spending weeks on route scouting just for an unexpected impurity to ruin a process. It can stop everything or even impact regulatory filings. The higher the purity, the fewer unknowns lurk in a new molecule. This compound doesn’t enter blockbusters or biologics, but it fits squarely in the path of specialty pharma and agrochemical pipelines. If the certificate doesn’t show rigorous testing—think residual solvents, heavy metals, and detailed melting point data—questions come fast. Colleagues who’ve sourced these halogenated benzonitriles for scale-up projects learned that a shortcut here risks the entire chain downstream, especially if used as a coupling partner in sensitive reactions.
Tackling the Supply Puzzle
Quality control isn’t just the job of an internal lab. It’s part of buying, inspecting, and trusting a supplier who cares about the product as much as the buyer. Global regulations—REACH in Europe, TSCA in the US—don’t just pop up for paperwork. They force a level of discipline that filters out dodgy sources. Reputable catalogs, usually based in Switzerland, Germany, or the United States, provide batch-specific analytical data. That direct access to traceability can keep one step ahead of costly failures. Vendors who invest in full CoA documentation and provide access to NMR, HPLC spectra, and elemental analysis win trust, especially when time and margins are tight.
Moving Forward: Smart Choices for Buyers and Labs
Reliable purity grades—ranging from analytical (98% and up) to the “extra pure” (over 99.5%)—give choices. In daily work, picking the highest grade doesn’t just impress quality auditors; it lowers waste, keeps surprises at bay, and builds confidence in every bottle. Initiating supplier audits, sampling incoming materials, and insisting on full documentation aren’t buzzwords—these are habits built from hard lessons in missed reactions and failed scale-ups. Only through persistent questions and sharp eyes can labs and companies keep their goals in reach.
Unpacking the Meaning of a CAS Number
Every time someone in chemistry or pharmaceuticals asks about a substance’s CAS number, they’re not just looking for trivia. They’re looking for accuracy and reliability, trying to sidestep the confusion that comes with long, complicated chemical names. The CAS number for 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile, a unique fingerprint in the chemical world, is 885271-10-3. I’ve seen firsthand how a single digit out of place in a chemical inventory can mean wasted hours, or even project failures, for researchers and businesses alike.
From the Lab Bench to Industry Databases
Most folks outside of chemistry circles roll their eyes at these long numbers, but anyone who's spent time in a lab knows they save time and avoid mistakes. I remember mixing up chemicals for a university project because my supplier sent the wrong compound – it looked nearly identical, but wasn’t. With a CAS number, you cut out mistakes like this. Think of it as the ultimate product code, ensuring everyone from the student to the factory foreman uses and gets precisely what they need.
Chemical suppliers rely on CAS numbers to label, ship, and track substances across borders and continents. In the case of 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile, that number points to one, and only one, thing. When you match the CAS number 885271-10-3, you’re not getting a guess; you get exactly what the order says, even if language barriers or naming conventions change.
The Stakes Behind the Digits
Mistakes with chemical identities can lead to real harm. Labs working on pharmaceuticals face tight safety regulations. Using a wrong chemical, due to a naming error or ambiguous abbreviation, risks contaminating medicine, setting back whole product lines, or worse, endangering lives. For companies racing to develop new drugs, the stakes run into millions of dollars. In environmental work, confusing one chemical for another can lead to faulty research and poor policy decisions with huge consequences for communities.
Years ago, I helped a startup set up their compliance system. Even with a smart, well-trained team, confusion crept in without clear identifiers. CAS numbers helped transform their inventory from chaos into order. Mistakes dropped, audits ran smoother, and trust with partners grew.
Challenges and Ways Forward
Not every chemical is as well-documented as 5-Bromo-2-chloro-6-fluorobenzonitrile. New substances appear faster than databases can keep up. Sometimes, finding a CAS number for a rare or recently synthesized compound isn’t straightforward. Digitizing lab records helps, but only if everyone maintains the same standards. Training matters too; people need to know why details like CAS numbers make a difference.
Scientists, manufacturers, and regulators started talking more in recent years about improving data sharing. Digital platforms that sync inventory with global databases help prevent costly mix-ups. Standardized digital recordkeeping can give every team member easy access to the exact information they need. Regularly updated training ensures that the new generation of chemists and technicians value precision as much as the experts before them.
Moving Beyond Simple Numbers
People put a lot on the shoulders of small identifiers like 885271-10-3. It’s a tiny detail, but it guards against disaster and waste. Whenever a new compound enters the scene, the first thing on my mind is whether it’ll get a CAS number – not for convenience, but to keep progress moving without avoidable setbacks. Small tools like this simplify a complex world and remind us that real progress comes from caring about the details.