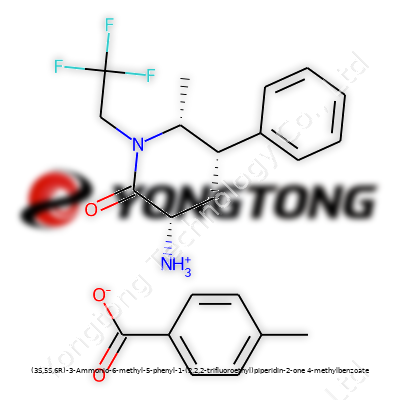
(3S,5S,6R)-3-Ammonio-6-methyl-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-2-one 4-methylbenzoate: A Deep Dive
Historical Development
Curiosity often drives progress, and the evolution of piperidinone derivatives tells a story of trial, error, and discovery. Chemists have tinkered with similar structures since the mid-20th century, especially as the pharmaceutical industry started pushing deeper into structure-activity relationships for nervous system disorders and rare enzyme targets. The rise of fluorinated organics in the late 1970s marked a new chapter, letting researchers play with trifluoroethyl groups to nudge activity and improve metabolic stability. The backbone for (3S,5S,6R)-3-Ammonio-6-methyl-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-2-one salts grew out of this practical need for more selective ligands. People in the know still swap stories about days hunched over rotary evaporators, chasing after pure crystalline forms, and comparing analytical notes on early batches of what would evolve into this 4-methylbenzoate salt.
Product Overview
Getting your hands on this compound isn’t like shopping for table salt. Its structure—anchored by a piperidin-2-one ring, decorated with a methyl and phenyl group, and further tweaked with a trifluoroethyl side chain and quaternary ammonium—draws attention for its potential as a synthetic intermediate or active pharmaceutical ingredient. The choice of 4-methylbenzoate as the counterion doesn’t just reflect solubility preferences. It also shapes its crystalline nature, improves handling, and sometimes, satisfies regulatory requirements in pharmaceutical systems. A quick glance at chemical suppliers shows this material catering mostly to early development or specialized pre-clinical pipelines in both Europe and North America, particularly wherever folks are looking to modify central nervous system activity or explore fluorinated motifs in lead optimization.
Physical & Chemical Properties
Holding a jar, the product looks off-white or faintly yellow, with fine crystalline or powdery consistency depending on crystallization. The compound’s melting point typically lands around 180°C, suggesting robust crystalline interactions yet avoiding major decomposition before analysis. The trifluoroethyl group does its job in shifting solubility profiles: the compound dissolves in DMSO, struggles in cold water, and shows limited solubility in most standard organic solvents. The ammonio group gives a persistent positive charge, and under most room temperature conditions, the compound stays hygroscopically stable. Chemical stability depends on keeping it away from strong bases or halogenating agents. The distinctive NMR and IR signatures—benzylic protons, piperidine ring signals, and a sharp CF3 stretch—ease purity checks for anyone with basic spectroscopic tools.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
The technical documentation reads as expected for high-end synthetic intermediates: purity often exceeds 98% by HPLC, single-point mass spectrometry matches, water content below 0.5%, and residue on ignition less than 0.1%. Labels list the full systematic name instead of shorthand, and batch-specific COAs accompany shipments—essential info for anyone in regulated industries. The product label typically includes recommended storage at 2-8°C in tightly sealed, moisture-resistant containers, expiration dates that hover around two years from synthesis, and UN transport codes for reactive organics.
Preparation Method
This is where theory meets practical headaches. The synthesis of (3S,5S,6R)-3-Ammonio-6-methyl-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-2-one runs through several strategic steps. The most common route involves a chiral amino alcohol precursor that gets cyclized, followed by N-alkylation with trifluoroethyl bromide. Stereochemistry needs tight control—the three stereocenters call for modern asymmetric catalysis or chiral pool approaches rather than old-school racemic resolutions to cut waste. The terminal ammonio group gets introduced by quaternarization, often under anhydrous conditions, before salt exchange introduces the 4-methylbenzoate anion. Running this process requires close monitoring, especially in the alkylation stages, since excessive base or temperature swings can throw off yields or torch stereochemistry.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
Nobody likes to talk about failures, but tweaking this molecule presents a handful of tough stops and starts. Direct modification of the phenyl group invites classic aromatic substitution—nitration or halogenation as the textbooks teach. The methyl node resists oxidation but can undergo halogen-promoted substitutions with care. The piperidinone ring itself supports N-dealkylations for those aiming to make downstream analogs, though yields can drop if catalysts aren’t fresh. On the experimental end, swapping the 4-methylbenzoate for other carboxylate salts opens up an avenue to test counter-ion effects or improve physical properties for specific routes. The trifluoroethyl branch gives good resistance to most common oxidants, fueling its appeal for downstream medicinal chemistry modifications.
Synonyms & Product Names
Language can trip up even experienced chemists. Some catalogs abbreviate this compound as “TFEP-Pip-4MeOBz” in internal documents. Others lean on IUPAC: (3S,5S,6R)-3-ammonio-6-methyl-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-2-one 4-methylbenzoate. In-house project codes at some research sites might mention “TFEP-Pipe” or similar short forms, which appear in unpublished reports and patents. Making a purchase or cross-checking references can turn annoying without confirming the stereochemistry and full salt name, which matters whenever regulatory agencies get involved or suppliers cross international borders.
Safety & Operational Standards
Every step in the handling of piperidinone compounds deserves respect. This molecule isn’t classed as highly toxic, but the trifluoroethyl fragment and quaternary ammonium core remind a chemist not to cut corners. Eye and skin protection count as non-negotiable, just as with any active pharmaceutical intermediate. Proper air handling keeps powder exposures low. Spills get swept, not blown or brushed, to avoid airborne dust. Waste management leans on incineration, not simple drain disposal, due to the potential for persistent organofluorines in waterways. Transport follows DOT and IATA rules for organics, especially for bulk shipments, reflecting modern standards in chemical stewardship. Audits typically focus on labeling, inventory accuracy, and review of worker training before regulatory signoff.
Application Area
It helps to know where a compound fits. This piperidinone derivative attracts interest from central nervous system research, where its unique combination of trifluoroalkyl and phenyl groups allows targeting of neurotransmitter systems and certain receptor subtypes. Drug design teams value it for scaffolding in lead optimization cycles. Folks in agrochemical discovery like the piperidine ring but tend to swap out the benzoate salt for different formulations, so crossover remains rare. There’s been some push in the development of imaging tracers, given the N-alkyl functionalities, yet regulatory hurdles for new radiotracers keep this use specialized. In research settings, its tangible stability during storage and on handling benches helps support method development for new synthetic routes and analog libraries.
Research & Development
I remember a research partner excitedly sharing NMR spectra for new analogs of this core—strong aromatic peaks, sharp doublets, and lots of room for derivatization. This hands-on excitement translates to continued exploration by medicinal chemists who see potential in optimizing selectivity and off-target binding. Publications sometimes spotlight SAR efforts using this scaffold, especially in targeting atypical dopamine or serotonin receptors. In silico modeling benefits from the trifluoroethyl group, whose electron-withdrawing impact factors into pKa shifts and lipophilicity tweaks. Ongoing collaborations with biochemistry units aim to unravel how different counter-ions impact absorption or protein binding, with several groups pushing for in vivo proof of concept for closely related scaffolds in animal models.
Toxicity Research
Toxicity questions keep popping up as with any synthetic intermediate: do the fluorinated side chains stick around in the body? Early pharmacology data suggests moderate oral bioavailability and limited acute toxicity in rat models, but sub-chronic and environmental fate require more work, especially before anything heads to full-scale animal trials. In aquatic toxicity panels, the benzoate portion breaks down fairly quickly, but the fluoroalkyl moiety demonstrates persistence—mirroring the challenges with related compounds flagged in the green chemistry movement. No genotoxicity alerts in screening models so far, though metabolism studies highlight slow clearance rates that demand attention before scaling up.
Future Prospects
Looking years ahead, expect this compound to play a bigger role in both CNS-focused drug discovery and broader synthetic chemistry toolkits. The trifluoroethyl group isn’t just a trendy side chain; it offers tangible differences in metabolic routes and tissue distribution, and, from what I’ve seen in the literature, the drive for metabolic stability only grows. Efforts to pivot this scaffold toward radiolabeled tracers or long-acting formulations keep showing up in grant proposals and biotech startup pitches. Its current formulation as a 4-methylbenzoate salt might not stay standard forever. As teams push for new formulations—less environmental persistence, more tailored tissue targeting—the core piperidinone keeps offering new surprises for both medicine and advanced chemistry challenges.
Understanding Purity in Real-World Lab Settings
Most people outside of chemistry circles glance at a label and trust whatever percentage is listed under "purity." In the lab, things rarely feel this simple. With compounds like (3S,5S,6R)-3-ammonio-6-methyl-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-2-one 4-methylbenzoate, a fancy name hides the real story: how close the actual sample comes to containing only the molecule you need. Every subtle contaminant will tell its own story, and in research, these impurities have wild consequences. I've seen reactions spiral into confusion because a single percent of leftover solvent or side-product interfered. That 98% or 99% on the bottle shouldn't lull anyone into a sense of security. Tiny traces of the wrong molecule change results, confuse spectra, and even hurt people if the product moves beyond the lab.
Scientific Fact: Purity Never Guarantees Certainty
Selecting a supplier for advanced drug-like molecules, especially something as niche as this chiral piperidin-2-one, involves a trust exercise built on reputation, documented quality, and rigorous analytical backup. Certificates of Analysis (CoA) provide some comfort, but always chase specifics: how did they measure that purity? HPLC often shows a clean peak and a magic number above 98%, but what lurks under the baseline? My own runs with LC-MS have spotted ghost peaks in otherwise “clean” materials. Broad-sweep methods sometimes miss structurally similar impurities, and with so many chiral centers in this compound, enantiomeric excess moves to the front of the line for scrutiny.
Why This Matters for Research and Health
Regulations for pharmaceutical precursors demand intense scrutiny. Impurities lead to toxic byproducts, unpredictable effects, and wasted research dollars. In one project, an untracked impurity derailed six months of experiments. We tend to learn the hard way that “almost pure” doesn’t cut it when transitioning from bench chemistry to preclinical or manufacturing scale. Even for academic work, journals and peer reviewers now ask hard questions about sample integrity. Synthetic chemists, analytical specialists, and project leaders get no free pass; each group depends on real details about what goes into a reaction or formulation. If the active ingredient in a biological assay carries trace contaminants, data may be misleading or worse, reproducibility vanishes altogether.
Pathways To Improvement
Plain talk helps more than marketing jargon here. Labs should regularly run orthogonal purity analyses: HPLC, LC-MS, and chiral chromatography. Sharing full spectra, not just summaries, increases trust. Transparency doesn’t just meet regulatory demands; it accelerates discoveries. Every chemist knows the weight of an ambiguous analytical report—so root out ambiguity. Push suppliers to release details on synthesis, isolation, and purification methods. Ask for residual solvent levels, heavy metals, and chiral purity. If the answer is vague, move on. Widespread adoption of open, detailed data in purchasing decisions protects people’s work, budgets, and health.
The Value of a Careful Eye
Chasing down pure samples, especially for complex chiral molecules, keeps science honest and productive. No one wants to explain to a colleague, backer, or regulator why their results spun off track—especially over invisible impurities that could have been flagged earlier. Only by treating chemical purity as a real, lived experience can researchers guarantee that the numbers on the bottle mean something when the rubber meets the road.
Why Storage Matters
Keeping products in the right place at home often makes a difference in how long they last and how safe they stay. Not every item can handle the same treatment. Some things lose their punch if they get too hot or too cold, and others turn bad simply through air or light. That’s nothing new, but it’s easy for folks to overlook these details during a busy week.
What Science Tells Us About Shelf Life
Many products, whether food or medicine, change when they’re exposed to sunlight, high temperatures, or moisture. Vitamins in orange juice break down if left out, and medicine tucked in a bathroom cabinet loses strength because moisture creeps in. Those chemical changes aren’t just theoretical: studies show vitamin C in juice stored at room temperature with light loses 50% of its potency in less than two weeks. So, a stable environment doesn’t just save money—it protects you and your family’s health.
Safe Storage Habits
Every kitchen or workshop has its own quirks: maybe the fridge pushes food to freeze in a certain corner, or the attic roasts items left for next year’s big cleanup. Keeping chemicals or cleaners in the garage over the summer introduces risks too. Labels usually suggest a cool, dry spot away from sunlight, and that comes from decades of reliability studies done by scientists. A regular shelf in the pantry, cleaned up so spills can’t mix, does better than storing cleaning liquids under the sink next to plumbing prone to leaks.
Personal Experience With Poor Storage
In my own apartment years back, I kept a bottle of acetaminophen in a bathroom drawer thinking it was out of reach. That place turned out to be a sauna every time someone showered, and the pills stuck together in clumps. Eventually, I learned the hard way: putting medicine on a high closet shelf far from pipes and humidity gave the tablets a long and useful life. That same logic works for batteries, too. Dropping them in a glass bowl by the stove caused them to corrode quickly. Sealed plastic containers in a dry place worked wonders instead.
Some Useful Facts and Solutions
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends medicine be kept between 68-77°F in a closed container away from light. Paint manufacturers suggest storing cans in places where temperatures never dip below 50°F or soar above 85°F. Many food items, once opened, benefit from refrigeration. Coffee beans left out at room temperature in a sealed, opaque jar keep aromatic oils much longer.
For families with little space, consider clear bins with labels and a simple inventory list taped inside a cabinet. Keep moisture-absorbing packets with electronics; seal food tightly before refrigerating. Check for expiration dates every few months, and discard items that smell or look off. This little effort leads to better use of your budget, fewer accidents, and healthier living.
Why the Package Matters
Talking with chemists and supply managers over the years, one topic always gets more attention than people outside the field expect: package sizes of compounds. If you work in a lab or manufacture products, the size of the container isn’t just a number on a product page; it sets limits and opens up possibilities for work, waste, and even compliance.
Small, Medium, Large: Who Gets What?
Small research labs run through just a few grams of a compound in a year. A huge barrel would overwhelm the space and turn into expensive waste the moment the compound goes past its shelf life. In places like startups, every dollar and square foot counts. We learned the hard way once when we bought a 25-kilogram drum, just to see most thrown away two years later. Folks in large manufacturing, though, see the opposite. A little bottle every week means a bureaucratic mess, endless tracking, and higher costs per gram. Bulk packages keep operations smoother, workers on task, and costs lower. That’s not theory; the purchasing numbers don’t lie.
Waste and Safety in the Mix
Old habits bite back. I’ve seen researchers split batches by hand from big containers, and all it takes is a moment’s inattention to break contamination protocols, leading to failed experiments or worse—a toxic incident. Products in the right size cut down those risks, and waste shrinks. In pharmaceutical settings, open a larger pack, and time ticks against the expiry clock. Multiple smaller options let teams open what they need, so none goes off before it is used.
Regulations and Responsibility
It’s not just scientists who care. Laws control how much of some substances can sit in one place—think fire marshals peering at storage logs, or the Drug Enforcement Administration showing up for anything with a controlled status. Small containers keep inventory within legal limits and make inspections less stressful. From the compliance perspective, cost isn’t the only argument. One business owner told me, “If I can buy the size that fits legal caps, my risk of fines and shutdowns disappears.” That isn’t a minor detail for a lab that might otherwise lose its license.
Delivering on E-E-A-T: Reliable Packaging Sources
With years of experience sourcing chemicals, one lesson stands out: not all suppliers carry the same size options. The best ones let you pick from something like 1 g to 100 kg, with certificates and batch data to back up what’s in the container. Reliable shipment tracking matters, too, especially with specialty materials that degrade with temperature or time. Buying from sellers who answer questions about packaging and can explain temperature controls has saved the day more than once. In the end, trust builds over repeat orders, honest answers, and clear documentation—critical for anyone subject to audits.
A Better Approach to Compound Distribution
Packaging choices go beyond preference; they shape safety, budget, and compliance. Flexible sizes help labs avoid wasting both money and valuable materials. Manufacturers, hospitals, and universities share this problem, just with different numbers. Suppliers who listen to end users add value—not just by selling a substance, but by delivering it in a way that works for real people. That’s good for labs, good for business, and, ultimately, a smarter way to support science.
Driving Change in Agriculture
Growing up near farming towns, I saw firsthand how even a single ingredient can transform a harvest. This chemical, known for its role in boosting plant growth, has become a key player for farmers wanting bigger yields. Many rely on it to help their crops suck up nutrients and resist pests. Some experts from the University of Florida have pointed out that applying it at the right time can make or break corn or wheat seasons. Overuse can backfire, so responsible application matters. Fresh data from USDA studies show that targeted use increases profits for mid-size farms.
Boosting Industrial Manufacturing
Walk through a modern factory, and you’ll notice chemical processes humming in the background. This substance is a workhorse in industries like plastics, textiles, and electronics. Manufacturers use it to clean surfaces, speed up reactions, and strip away unwanted residues. I once toured a plastics facility near Chicago; the foreman explained that skipping this step meant dealing with lower-quality batches, costing both time and money. In electronics, this compound ensures microchips stay free from contaminants, helping slim devices run without hiccups. Years of industry data from Statista chart a steady expansion in demand as production ramps up worldwide.
Cleaning Up in Healthcare Settings
Hospitals can’t cut corners on hygiene, and this chemical plays a quiet yet crucial role in maintaining sterile environments. Medical centers have turned to it as a disinfectant, using it to wipe down equipment and make surgical tools safe. One CDC report highlights its proven track record in killing bacteria and viruses without corroding sensitive tools. From conversations with hospital sanitation staff, it’s clear that having an effective agent streamlines daily cleaning routines and reduces the risk of infection. The World Health Organization actually includes it in its lists of recommended cleaning agents.
Protecting Our Food Supply
This ingredient helps keep food fresher for longer once it leaves the farm. Processors add tiny amounts to packaging or cleaning solutions to stop mold and bacteria from spreading. I spoke to a manager at a food packaging plant, who described its role as “an invisible shield” for products like cheese or pre-cut fruit. Food safety authorities like the FDA keep strict limits on how much can be used, and regular testing backs up its safety. A review from the Food Quality and Safety Journal underlines how careful handling can cut spoilage and reduce food waste.
Moving Toward Greener Solutions
Of course, not everyone cheers chemical fixes. There’s a visible push for alternatives that are kinder to the planet. Green chemistry journals highlight ongoing research into similar compounds that break down faster once released. Some companies now recycle the chemical after use, reducing runoff that can harm nearby streams or groundwater. Consumers asking tough questions put pressure on producers to be transparent about sourcing and disposal practices. Building on my own work in environmental policy circles, I’ve seen success when regulators and manufacturers actually talk to each other and set shared goals for cleaner production cycles.
Looking Ahead
Smart, targeted use of chemicals like this won’t solve every problem, but ignoring their real advantages would be short-sighted. Progress means seeking out every opportunity to improve practices, cut waste, and drive innovation—without risking long-term health or environmental safety. With more investment in research and a willingness to adapt, the next chapter for this compound could be even more surprising.
The Reality Behind “How Soon Can I Get My Order?”
Anyone who’s waited for an online purchase knows that shipping lead time isn’t just a number—it’s the gap between wanting something and actually holding it. In business, this period can test patience and influence big decisions. The phrase ‘lead time for shipping’ might sound straightforward, but those days or weeks aren’t picked out of thin air. Real people, real processes, and real challenges shape them.
What Shapes Shipping Lead Time?
Warehouses don’t work like magic factories. Staff must pick items, package them, schedule pickups, and get them out the door. Every step stacks up. Something as simple as a late supply truck or a sudden spike in orders means your item could take longer to leave the shelf. I’ve watched teams scramble during holiday rushes as pallets pile up, knowing customers are refreshing tracking numbers every hour. A moment of delay at any point makes a difference.
The distance between warehouse and front door matters, too. Sending a package across town, the journey might just take an afternoon. Ship overseas, and things get complicated. Carriers juggle customs paperwork, weather delays, and clogged ports. Add a global pandemic or a worker strike, and timelines fall apart. I once waited three months for parts from Asia because a port got jammed up—it’s enough to make anyone rethink their supply chains.
Why Lead Time Impacts More Than Your Patience
Fast shipping isn’t just about convenience. For businesses, lead time can make or break the bottom line. If a factory runs out of key parts, production stops. If shelves stay empty, customers turn elsewhere. I’ve seen stores try to predict seasonal shopping flurries and get burned by guessing wrong. Order too little, and they lose sales; order too much, and inventory sits, tying up cash that could fund the next big thing.
Some shoppers act like a slow shipment hints at a careless company. Truth is, every minute shaved off lead time takes planning, money, and trust in partners. The world’s biggest companies spend millions building networks of warehouses closer to customers, just so delivery trucks have fewer miles to travel. That investment pays off in loyalty and repeat business. Amazon’s two-day promise didn’t happen by accident—it emerged from years of relentless work and feedback from customers who hate waiting.
What Can Be Done to Improve Lead Times?
Clear communication always helps. Companies that set honest expectations and keep customers updated turn a long wait into a manageable one. Smart technology makes a real difference, too. Inventory tracking, automated ordering, and precise forecasting stop problems before they start. I’ve seen supply managers rely on tools that give real-time alerts if things get off track, which means they can pivot and solve problems faster.
Forging strong relationships with shipping providers goes a long way. When trouble hits, those connections bring flexibility—faster reroutes, priority handling, or alternate transport. Some solutions aren’t glamorous, just solid: keeping extra stock on hand, expanding local delivery teams, or simplifying the product lineup to reduce headache.
Experience Shapes Expectations
Shipping lead time isn’t just a number to plug into a website. Every package tells the story of human effort, weather, distance, and planning. For businesses and buyers alike, recognizing that story turns a frustrating wait into an opportunity to adapt, improve, and maybe even show a little empathy along the way.