1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide: A Ground-Level Look at Its Journey and Uses
Historical Development
Development of 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide reflects steady progress in synthetic chemistry throughout the last century. Often, research in pyrazole chemistry built on aspirations to create molecules that merged stability with reactivity. Laboratories searching for selective functionalization methods in the 1960s and 1970s noticed patterns in pyrazole scaffolds, aware of how a simple methyl group tweak could shift biological and industrial characteristics. By the late 1980s, demand for new sulfonamides as crop protection agents or intermediates in pharmaceuticals expanded the reach of the humble pyrazole. Conversations among scientists reveal that the pursuit often required months of iterative work, purifying samples and mapping reactivity pathways, all undertaken with practical lab protocols rather than automated screens.
Product Overview
Over time, 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide gained a foothold due to its adaptable structure, allowing for substitution reactions that can deliver better performance in both industrial and academic settings. Chemists value this compound for combining sulfonamide functionality with the robust pyrazole ring. Its appearance in product catalogs signals recognition not just for its reactivity but for how it bridges academic research and manufacturing. This molecule now serves as a middleman between invention on the bench and application in large-scale synthesis—a quiet workhorse in the toolkit for many fields including agricultural chemistry, medicinal research, and polymer science.
Physical & Chemical Properties
Density, melting point, appearance, and solubility make or break a compound’s real-world reputation, and 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide covers the basics. Typically, the compound appears as a crystalline solid, white or off-white. Its melting range sits firmly above room temperature, eliminating the messiness that comes from sticky intermediates in a reaction flask. Solubility generally leans toward polar solvents, something I appreciated in the lab, as it simplified both isolation and purification. Water brings modest solubility, but common organics like ethanol or acetone offer better performance. Chemical stability owes much to the pyrazole’s aromaticity, preserving the core even under mild heat or slightly acidic or basic conditions.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Regulatory and supplier standards reflect a shift in thinking over recent decades. Clear labeling of 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide extends beyond the basics of purity and batch number. Suppliers include comprehensive safety data sheets featuring hazard symbols and detailed storage instructions. Labels spell out concentration limits, crystal habit, and storage conditions—room temperature, dry place, tightly sealed. Some vendors provide detailed chromatograms, a nod to academic and industrial pressure for reproducibility and trust. Compliance now shapes the entire journey, from bench to bottle, giving researchers reassurance on identity and traceability as they design new processes or products.
Preparation Method
Synthesis often starts with methylation of the appropriate pyrazole, followed by sulfonation at the 4-position, which traditionally requires control of temperature and acidity. These steps use routine reagents and time-tested glassware. I have watched skilled technicians optimize the reaction by adjusting the sulfonating agent or tweaking temperature profiles, looking for higher yield with fewer byproducts. Years ago, syntheses depended on trial, error, and patience, but modern routes harness microwave techniques and safer sulfonation conditions. The chemistry speaks to resilience: if one method falters, another often patches the gap with only minor losses. Work-up involves extraction, crystallization, and drying—a familiar sequence to anyone handling small heterocyclic sulfonamides.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
This compound offers a reactive canvas for further chemistry. The methyl groups on nitrogen serve as protective groups or anchor points for further substitutions. Researchers use nucleophilic aromatic substitution to install new functional groups at available positions, expanding the derivative library. The sulfonamide moiety stands out in both stability and reactivity, partnering easily with strong bases or electrophilic reagents. Functionalization of the sulfonamide often involves reacting with chlorinating agents or organometallics under controlled temperature and pH—a process learned and shared across research groups. With each tweak, the properties adapt, opening up variants for testing in new applications or fine-tuning for regulatory compliance.
Synonyms & Product Names
Beyond the formal mouthful, the compound circulates under trade names and synonyms that reflect either its function or its structure. In laboratory purchase orders, you may see “4-Sulfonamide-1,3-dimethylpyrazole,” or abbreviated as “DMPZSA.” Catalog listings sometimes reference “N,N-dimethylpyrazole-4-sulfonamide.” Variations draw on supplier preferences, but the chemical backbone remains. These aliases allow cross-referencing in literature or supply chain documents, saving researchers time and minimizing ordering errors that might derail an experiment. I have come to recognize the value in knowing all the names; sometimes, results hide in a reference under a synonym, not an official IUPAC descriptor.
Safety & Operational Standards
A responsible chemical operation centers on risk management. Data from safety data sheets and regulatory advisories call for gloves, goggles, and suitable ventilation during handling. Experience teaches respect for finely divided powder, which can irritate the throat and skin on contact. Disposal aligns with hazardous waste guidelines to avoid environmental contamination, echoing increasing social emphasis on chemical stewardship. Storage in a dark, cool, and dry place sidesteps degradation. Thorough training and shared protocols anchor safety culture in both industrial and academic labs, preventing exposures that lead to both short-term symptoms and long-term health risks.
Application Area
Agricultural scientists often look to 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide as a nitrification inhibitor, helping slow soil nitrogen loss. In my interactions with agronomists, there’s acknowledgment of how this compound’s stability under field conditions makes it reliable even in difficult weather or highly variable soils. Crop protection benefits from tailored formulations that reduce volatilization and leaching, cutting both costs and environmental burden. Medicinal chemistry projects sometimes investigate sulfonamide derivatives for their bioactivity, leveraging this solid core for anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial agents. Outside of these, its derivatives find occasional use in material science, supporting the synthesis of specialized polymers or resins.
Research & Development
Research runs on both curiosity and economic push. For years, teams have focused on refining synthesis to minimize byproducts and waste, building on both academic know-how and industry feedback. Ongoing studies track the fate of 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide in soil, water, and biological systems, trying to balance performance against persistence in the environment. Recent advances include work on automated synthesis and predictive modeling, which help forecast how new variants might behave before they hit the bench. Collaborative efforts between universities and manufacturers drive innovation, with some teams using high-throughput screening to spot promising leads or to flag troublesome side products.
Toxicity Research
Toxicology research draws a line between utility and harm. Data from laboratory rodents and environmental models show that acute toxicity sits within manageable bounds at typical use concentrations, though real-world application brings greater complexity. Low-dose chronic exposure studies receive plenty of attention, especially regarding soil health and aquatic ecosystems. Screening for endocrine disruption or mutagenicity represents both duty and precaution, prompted by increasing regulatory scrutiny. Many scientists work with independent third-party testing groups to check for unexpected metabolites or breakdown products, learning from both controlled trials and field runoff analysis. Conversation and debate continue over safe exposure thresholds, often leading to adjustments in recommended handling and application methods.
Future Prospects
Development does not stand still. Pressures to reduce environmental impact push research toward finding biodegradable alternatives, novel delivery systems, or safer process chemistries. Incentives encourage greener chemistry: if a synthetic route generates less waste or avoids hazardous intermediates, adoption follows quickly. Some pharmaceutical projects eye sulfonamide-rich scaffolds for new drug development, given the track record of related molecules in medicine. Regulatory trends push companies to maintain transparency, bringing extra trust but also extra paperwork. I see industry and academics sharing data more freely, accelerating the feedback loop that brings safer, more effective products to market. The next decade promises further advances, as each research cycle adds hard-earned knowledge to the old chemistry playbook, refining both the science and the culture around it.
Why 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide Draws Attention
People often look at chemicals in fertilizers with some skepticism. Some names sound intimidating, and 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide is no exception. Still, this compound has an important role in how modern food production works, along with helping the environment in ways folks might not expect.
A Look at Agriculture’s Relationship with Nitrogen
Farmers depend on fertilizers to feed growing crops, especially when working with corn, wheat, and other big staple foods. Standard nitrogen fertilizers, like urea and ammonium-based types, offer essential nutrients. But these nutrients don’t always stay put. Rain and soil bacteria change nitrogen into forms that easily wash away, run into rivers, or pump nitrous oxide into the air. That’s where the trouble begins, causing both economic loss for growers and real damage to water supplies and climate.
So, Where Does This Chemical Fit?
1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide, known among agronomists as DMPP, acts as what’s called a nitrification inhibitor. It doesn’t add nutrients. Instead, DMPP helps lock nitrogen in the ammonium form for a longer stretch of time in the soil. It puts the brakes on the soil bacteria that turn ammonium into nitrate, the form that loves to run off in a hard rain or sneak away into the air.
There’s real science behind the use of DMPP. Trials across Europe and North America show fertilizers treated with DMPP lead to less nitrate leaching from soils. By slowing the nitrification process, roots get a more steady supply. Farmers often see better yields and they spare themselves the cost of replacing nitrogen that’s floated off before plants could use it. Cleaner groundwater and lower greenhouse gas emissions can result from this shift.
Health, Water, and the Bigger Picture
Having spent time working on a family farm, it’s clear that fertilizers make or break a season. But higher yields come with heavy costs when rivers turn green from runoff algae, or folks in rural towns find contamination in wells. Every year, environmental agencies warn about rising nitrate levels, which link closely to health risks in newborns and long-term problems in fish habitats.
By making nitrogen fertilizers “smarter”—not just stronger—DMPP lets agriculture keep up with growing demand without poisoning the water we all rely on. Reducing nitrous oxide, a powerful greenhouse gas, aligns this approach with climate science. On both family farms and mega-operations, using inhibitors like DMPP balances the reality of feeding people and protecting natural resources, instead of choosing one over the other.
Future Outlook: Smarter Choices on the Field
Growing the food everybody eats sometimes means hard trade-offs between profit and environment. Innovations like DMPP shift the balance back toward sustainability. It doesn’t solve everything—farmers still need education, access to better products, and incentives to move away from dumping more fertilizer when it disappears. Policy has a part to play. Research and outreach can help small growers see the benefit, not just the up-front cost.
In my own work, the move to DMPP and similar compounds reflects a broader understanding: chemicals aren’t all bad, but using them wisely often leads to the best results on and off the farm. Tools like DMPP give reason for optimism in agriculture’s next chapter, where better management can serve both people and the land.
Looking Closer at 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide
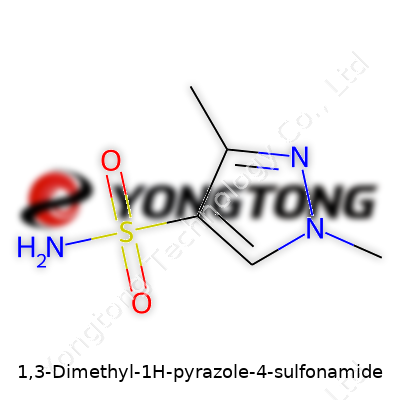
The chemical formula for 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide is C5H9N3O2S. Seeing a formula laid out like that probably brings back images of high school chemistry, flasks bubbling away on the bench, and the sharp smell of lab air. It’s one thing to know the formula, but understanding what makes up each part and why it matters—that’s where things get interesting.
Shaping Everyday Chemistry
Chemistry makes up the material world, and molecules like 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide don’t just live on dusty shelves in research labs. These compounds help drive agricultural technology, medicine, and sometimes improvements in industrial safety. This one, for example, pops up as an intermediate in crop protection chemicals and has carved out a quiet niche for itself in chemical synthesis.
The backbone of this molecule, the pyrazole ring, packs two nitrogen atoms at adjacent positions. These nitrogen atoms unlock several interesting properties—boosting stability and giving chemists room to build more complex molecules. N-methyl groups at positions 1 and 3 nudge reactivity and solubility just enough to make this molecule useful in a lab or in a tank on a farm. That SO2NH2 group, the sulfonamide, brings a thumbprint of reactivity. The sulfonamide group shows up again and again in molecules that fight bacteria or tamp down enzyme activity in plant and animal systems.
Trust and Transparency
Chemists rely on accurate formulas, not just for curiosity. Lab safety, environmental impact assessments, and regulatory paperwork all rest on simple numbers matching up with what a flask holds. I’ve worked in labs where a missed formula led to days of wasted time and even a close call with hazardous waste. Sharing solid, fact-checked information about these formulas matters. Without it, risks go up fast, and scientific progress takes a hit.
The Real-World Pressure
Out in the field, a compound like this might end up on a checklist for chemical registration. If it slips through with a wrong label or a missing nitrogen, local ecosystems or workers’ health hang in the balance. Accurate reporting of structures and their formulas gives researchers, regulators, and the public a shared foundation for action.
Transparency in chemical information answers real needs—clear labeling and access to safety data sheets, detailed documentation for environmental studies, and honest lists for medical surveillance of workers. I’ve seen what happens when companies skimp on this—tracing exposure becomes a headache, and trust between local communities and industry evaporates.
Solutions: Getting It Right Every Time
In my experience, the best way forward relies on open databases and third-party validation. Double-checking every formula before it goes public, cross-referencing with trusted chemical registries, and making results available to everyone—not just experts behind paywalls—helps create confidence. Employers, researchers, and even worried neighbors deserve clarity about what comes out of the lab and onto the land.
In the end, a string like C5H9N3O2S contains more than atoms—it holds responsibility and trust. Getting the formula correct and sharing it freely helps the entire chain—from the bench chemist working on crop safety to the community reading about new sprays in the news—take informed steps into the future.
Understanding the Compound
Anyone who works with chemicals in a lab or manufacturing setting knows storage isn’t just a checklist item – it’s a crucial part of safety and quality. 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide sounds like something straight out of a graduate textbook. Under that complex name sits a solid that lives in bottles in labs and warehouses around the world. Despite its low profile, this chemical brings plenty of opportunity in areas like crop protection and materials research, but only if it's handled with respect for the science behind it.
Temperature Means Everything
Store this compound with care. I’ve seen what a neglected storeroom can do to a seemingly stable material: clumps, odd smells, ruined batches. Temperature sits high on the list of things to watch. Room temperature, ideally between 20 and 25°C, gives this chemical the quiet life it prefers. Higher temperatures nudge substances toward slow breakdown. Lower temperatures may sound safer, but freezing and thawing can form water droplets inside containers, introducing moisture and making clumps that ruin solubility and purity.
Humidity – A Hidden Enemy
Moisture loves to creep where it shouldn’t. Even in tightly sealed bottles, a humid room can let water vapor slip in every time you open the lid. Over weeks or months, this can matter. Excess moisture can promote hydrolysis, quietly degrading the compound. The trouble goes beyond lost potency: sometimes, you get byproducts that gum up equipment or interact in unpredictable ways during experiments or production runs. A dehumidifier or keeping containers in a cabinet with silica gel pouches can make a difference. Dry hands, dry workspace, dry air: all three count.
Light and Air Aren’t Neutral
Sunlight looks harmless but packs energy that can slowly change chemical structures. Like many organics, 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide should avoid direct sun or harsh fluorescent bulbs. Opaque bottles or a dark storage cabinet do the trick. Oxygen can do its own damage, reacting with some compounds over time. Keeping lids screwed tight, using small bottles, and flushing headspace with an inert gas like nitrogen if containers will sit for months: these habits protect both your wallet and your data.
Labeling and Segregation
In a shared space or a busy lab, labeling matters as much as storage conditions. A faded marker and peeling sticker can make for expensive or dangerous mistakes. I write the receive date, my initials, and the exact chemical name big and clear. This is partly pride and partly insurance. Never mix this chemical with strong acids, bases, or oxidizers, even across the room. Separate shelves for each hazard class reduce headaches and risk of cross-contamination, which is rarely just a theoretical problem — spills and splashes happen.
Accidents Invite Attention
One bad experience with a degraded batch has people talking all week – especially if it leads to smoke, odd colors, or a brief lockdown. Regulations like OSHA and GHS weren’t built on empty worries. Material Safety Data Sheets recommend gloves, safety glasses, and working with chemicals like this in a fume hood or well-ventilated room. Those steps protect not just people, but also the compound slumbering in its bottle, waiting to be useful instead of hazardous.
Building Better Habits
There’s no shortcut for good habits in storage. Good shelves, organized cabinets, legible labels, regular checks, and a simple log notebook cover most risks. Training new team members goes beyond handing them a manual – it’s daily reminders and showing by example. If you care for 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide, it delivers reliable results. Forget the details, and you might lose both data and dollars. Responsibility here isn’t about red tape – it’s about making every gram count.
What We Know About 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide
If you care about chemical safety in farming, construction, or research, it makes sense to wonder whether a compound like 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide puts workers or bystanders at risk. This compound, sometimes called DMPSA, usually shows up in fertilizer enhancers. These additives help slow down how fast nitrogen gets released, which cuts down on runoff and keeps farmland more productive. But there’s more to the story than just chemistry on a label.
Health and Environmental Concerns
People ask about toxicity because chemicals often surprise us. Some are harmless until breathed in or mixed with water. Others, like certain solvents or pesticides, can cause problems after long-term exposure. Most current data suggests DMPSA itself doesn’t break records for acute toxicity. Rats taking in large doses by mouth only saw mild symptoms, and skin or eye contact showed limited irritation in most tests reported by manufacturers and EU chemical agencies. This sounds reassuring, yet these results only paint a partial picture. Much of the testing focuses on short-term exposure, which might not tell us enough about what low doses over years might do to people or local ecosystems.
Looking Deeper at Long-Term Safety
Public safety leans heavily on reliable toxicology. For compounds like DMPSA, long-term studies are rare. Some chemicals look safe in a lab or after one-time exposure, but can build up in animals, soils, or even water supplies. Without transparent, published research on whether DMPSA breaks down easily, moves through groundwater, or lingers in crops, farmers, regulators, and nearby communities miss out on crucial details. The European Chemicals Agency does list the product, but information on chronic effects, bioaccumulation, or interactions with other common field chemicals doesn’t jump off the page.
Practical Experience in the Field
People using DMPSA products tend to care about protecting their health. Farmworkers sometimes see companies push out new coatings or inhibitors with little hands-on guidance. Gloves and basic protective gear cut down risk for the skin and eyes. But inhaling dust or fine spray—even from something considered "low-toxicity"—can aggravate asthma or cause headaches. Some neighbors and field scientists have started testing runoff and soil for unbroken additives. That shows people don’t just rely on safety data sheets (SDS) but want independent assurance that today’s “low risk” status won’t turn into tomorrow’s problem.
Paths to Safer Use and Better Accountability
Producers could offer more rigorous, third-party toxicology reports. These should check not only what a chemical does in rats—but what happens to local insects, worms, birds, or fish. Real, accessible risk data matters more than fine print hidden in shipping documents. Local and national regulations set basic standards, but community feedback often catches bad news early, as seen with other agronomic chemicals in the past. Clear labeling, streamlined reporting if accidents occur, and quick translation of complex safety information into layman’s terms make a difference in practice. The only way trust grows is if community health, worker safety, and environmental impact don’t play second fiddle to speed or cost savings.
Farmers face tough choices balancing yield and stewardship. Many try to cut back on any possible hazardous input, especially if alternatives exist, or bring in outside labs to check residues themselves. This approach shows respect for land, food, and rural livelihoods. Until broader research fills in big gaps, anyone in contact with DMPSA should take standard precautions, back up claims with science, and push companies and regulators to improve public access to long-term safety studies.
Understanding What You’re After
There’s a lot of curiosity about buying chemicals like 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide. It's often paired with a hunt for reliability and, honestly, peace of mind. People use this compound in projects linked to chemical synthesis, crop protection, or specialty research, and care about both safety and legality in the supply chain.
Trust Over Convenience: Picking Suppliers
In my own work with research labs, I saw frequent reliance on suppliers who earned trust the hard way: through years of consistent deliveries and open communication about sourcing. Supply houses like Sigma-Aldrich, Alfa Aesar, and TCI America have long shipping records for academic and industrial buyers. They require valid business or research credentials, and they take safety and compliance checks seriously. If you see these names on a list, you expect transparency about purity, technical sheets, and shipping limitations. Most researchers know that reliable chemical vendors never ask for cash up front with no paperwork, and they always expect verification of intent and identity.
The Grey Area: Online Marketplaces
You might feel tempted to chase obscure deals from online marketplaces or third-party sites. Listings claiming to supply this chemical sometimes skip details about purity grades, batch history, or legal restrictions. I've run into these advertisements, and every time I see a vague description and no certificate of analysis, it’s a big red flag. Buying from these kinds of sellers runs risks, not just for quality, but also for safety and compliance with local regulations. Some buyers find themselves with an expensive bottle of something that’s not even the right compound or, worse, with legal trouble.
Safety and Legal Responsibility
There’s more at stake than just getting the right stuff. Regulatory bodies like the EPA, OSHA, and local customs offices monitor the movement of specialty chemicals in most countries. The responsibility falls on both the seller and the buyer: you have to know the laws about storage, handling, and shipping of chemical agents. Hazard studies and safety data sheets don't just make paperwork thicker—they help you keep your team and workplace safe. I’ve watched an experienced chemist refuse shipment from an unknown supplier because certain documentation went missing. That’s the kind of decision that prevents bigger problems down the line.
Smart Shopping: Questions to Ask
If you're after 1,3-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-sulfonamide for legitimate research, ask for proof. Vendors should show transparency about where and how they produce or source the compound. Always request a certificate of analysis and safety data sheet before purchase. Genuine suppliers welcome these questions and provide clear batch and storage data. If you need large volumes or special handling, work with a supplier that customizes shipping and storage—never settle for a generic label or codename in the catalog.
The Path Forward
Science and industry need strong supply networks. Reliability in the chemical marketplace grows when buyers choose documentation over price wars. It makes a difference for safety, for the environment, and for the integrity of your results. So, consult with established vendors who respect the rules, keep your paperwork in line, and never buy from someone who seems eager to skip the details.